Activation of the proton-sensing GPCR, GPR65 on fibroblast-like synoviocytes contributes to inflammatory joint pain
- PMID: 39661058
- PMCID: PMC11665855
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2410653121
Activation of the proton-sensing GPCR, GPR65 on fibroblast-like synoviocytes contributes to inflammatory joint pain
Abstract
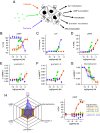
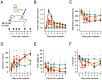
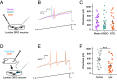
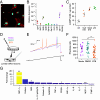
Inflammation is associated with localized acidosis, however, attributing physiological and pathological roles to proton-sensitive receptors is challenging due to their diversity and widespread expression. Here, agonists of the proton-sensing GPCR, GPR65, were systematically characterized. The synthetic agonist BTB09089 (BTB) recapitulated many proton-induced signaling events and demonstrated selectivity for GPR65. BTB was used to show that GPR65 activation on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), cells that line synovial joints, results in the secretion of proinflammatory mediators capable of recruiting immune cells and sensitizing sensory neurons. Intra-articular injection of BTB resulted in GPR65-dependent sensitization of knee-innervating neurons and nocifensive behaviors in mice. Stimulation of GPR65 on human FLS also triggered the release of inflammatory mediators and synovial fluid samples from human osteoarthritis patients were shown to activate GPR65. These results suggest a role of GPR65 in mediating cell-cell interactions that drive inflammatory joint pain in both mice and humans.
Keywords: GPCR; acidosis; arthritis; inflammatory pain; nociception.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
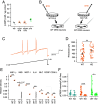
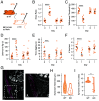
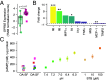
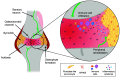
References
-
- Ghouri A., Conaghan P. G., Treating osteoarthritis pain: Recent approaches using pharmacological therapies. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 37 Suppl 120, 124–129 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Andersson S. E., Lexmüller K., Johansson A., Ekström G. M., Tissue and intracellular pH in normal periarticular soft tissue and during different phases of antigen induced arthritis in the rat. J. Rheumatol. 26, 2018–24 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Sasaki Y., Hada R., Nakajima H., Fukuda S., Munakata A., Improved localizing method of radiopill in measurement of entire gastrointestinal pH profiles: Colonic luminal pH in normal subjects and patients with Crohn’s disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 92, 114–8 (1997). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 225856/Z/22/Z/Wellcome Trust (WT)
- NF\R2\212001/Royal Society (The Royal Society)
- BB/V509528/1/UKRI | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- 21530/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- MR/P021220/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/MO11194/1/UKRI | Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC)
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G104108/AstraZeneca (AstraZeneca PLC)
- MR/W002426/1/UKRI | Medical Research Council (MRC)
- N/A/cambridgeuniversity | Corpus Christi College, University of Cambridge (Corpus Christi College)
- MR/W026961/1/UKRI | Medical Research Council (MRC)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

