The adenine nucleotide translocase family underlies cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury through the mitochondrial permeability pore independently of cyclophilin D
- PMID: 39661674
- PMCID: PMC11633734
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adp7444
The adenine nucleotide translocase family underlies cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury through the mitochondrial permeability pore independently of cyclophilin D
Abstract
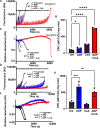
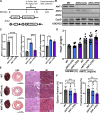
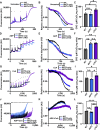
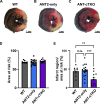
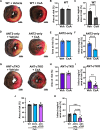
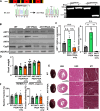
The mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) is implicated in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. During I/R, elevated mitochondrial Ca2+ triggers mPTP opening, leading to necrotic cell death. Although nonessential regulators of this pore are characterized, the molecular identity of the pore-forming component remains elusive. Two of these genetically verified regulators are cyclophilin D (CypD) and the adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) family. We investigated the ANT/CypD relationship in mPTP dynamics and I/R injury. Despite lacking all ANT isoforms, Ca2+-dependent mPTP opening persisted in cardiac mitochondria but was desensitized. This desensitization conferred resistance to I/R injury in ANT-deficient mice. CypD is hypothesized to trigger mPTP opening through isomerization of ANTs at proline-62. To test this, we generated mice that expressed a P62A mutated version of ANT1. These mice showed similar mPTP dynamics and I/R sensitivity as the wild type, indicating that P62 is dispensable for CypD regulation. Together, these data indicate that the ANT family contributes to mPTP opening independently of CypD.
Figures


References
-
- Bernardi P., Gerle C., Halestrap A. P., Jonas E. A., Karch J., Mnatsakanyan N., Pavlov E., Sheu S.-S., Soukas A. A., Identity, structure, and function of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore: Controversies, consensus, recent advances, and future directions. Cell Death Differ. 30, 1869–1885 (2023). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karch J., Kwong J. Q., Burr A. R., Sargent M. A., Elrod J. W., Peixoto P. M., Martinez-Caballero S., Osinska H., Cheng E. H., Robbins J., Kinnally K. W., Molkentin J. D., Bax and Bak function as the outer membrane component of the mitochondrial permeability pore in regulating necrotic cell death in mice. eLife 2, e00772 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

