Invasive Group B Streptococcus Infections Caused by Hypervirulent Clone of S. agalactiae Sequence Type 283, Hong Kong, China, 20211
- PMID: 39662881
- PMCID: PMC11682793
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3101.231627
Invasive Group B Streptococcus Infections Caused by Hypervirulent Clone of S. agalactiae Sequence Type 283, Hong Kong, China, 20211
Abstract
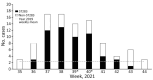
During September-October 2021, group B Streptococcus bloodstream infections surged among patients hospitalized in Hong Kong. Of 95 cases, 57 were caused by the hypervirulent strain sequence type 283, which at the time was also found in freshwater fish and wet market environments and thus poses a transmission threat.
Keywords: China; GBS; Hong Kong; ST283; Streptococcus agalactiae; bacteremia; group B Streptococcus; meningitis; molecular epidemiology; pyogenic arthritis; sepsis; streptococcal infections; streptococci.
Figures

References
-
- Barkham T, Zadoks RN, Azmai MNA, Baker S, Bich VTN, Chalker V, et al. One hypervirulent clone, sequence type 283, accounts for a large proportion of invasive Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from humans and diseased tilapia in Southeast Asia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13:e0007421. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007421 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

