Dual antiplatelet versus alteplase in anterior and posterior circulation minor stroke
- PMID: 39663175
- PMCID: PMC12415641
- DOI: 10.1136/svn-2024-003705
Dual antiplatelet versus alteplase in anterior and posterior circulation minor stroke
Abstract
Objective: The Antiplatelet versus R-tPA for Acute Mild Ischaemic Stroke trial has demonstrated the non-inferiority of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) to alteplase in minor non-disabling stroke. This prespecified secondary analysis aimed to investigate whether the treatment effects were similar across stroke territories.
Methods: Participants were divided according to stroke territory, which were subdivided into DAPT and alteplase. An excellent functional outcome at 90 days defined as modified Rankin Scale scoring 0-1 was primary outcome. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score change and early neurological improvement measured by a 2-point decline in NIHSS score at 24 hours were secondary outcomes. Symptomatic intracerebral haemorrhage (sICH) and bleeding events were safety outcomes. Primary analyses adjusted unbalanced baseline characteristics between treatments by multivariate logistic regression.
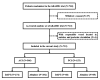
Results: A total of 719 patients were included: 566 in anterior circulation stroke (ACS) and 153 in posterior circulation stroke (PCS). Primary outcome was 94.1% in DAPT and 91.7% in alteplase among ACS patients (adjusted risk difference (RD) and 95% CI, 1.5% (-1.5% to 4.6%), p=0.32), while 91.2% in DAPT and 91.8% in alteplase among PCS patients (adjusted RD and 95% CI, -2.1% (-8.5% to 4.4%), p=0.53). Compared with alteplase, DAPT was associated with lower risk of sICH (p=0.03) and bleeding events (p<0.001) in ACS, but only lower risk of bleeding events (p=0.007) in PCS. Additionally, among ACS patients, the alteplase was superior to DAPT in terms of decrease in NIHSS score at 24 hours compared with admission (adjusted geometric mean ratio and 95% CI, -0.09 (-0.16 to -0.03), p=0.005) and early neurological improvement (adjusted RD and 95% CI, -7.2% (-11.6% to -2.7%), p=0.001).
Conclusion: Among ischaemic stroke with minor non-disabling symptoms, DAPT was similar with intravenous alteplase regarding long-term functional outcome and better safety regardless of ACS or PCS. The potential benefit of intravenous alteplase regarding early neurological improvement in patients with ACS warrants further investigation.
Trial registration number: NCT03661411.
Keywords: Cerebrovascular Circulation; Ischemic Stroke; Stroke; Thrombolysis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50:e344–418. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Chen W, Zhou H, et al. Chinese Stroke Association guidelines for clinical management of cerebrovascular disorders: executive summary and 2019 update of clinical management of ischaemic cerebrovascular diseases. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020;5:159–76. doi: 10.1136/svn-2020-000378. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
