Placenta-tropic VEGF mRNA lipid nanoparticles ameliorate murine pre-eclampsia
- PMID: 39663452
- PMCID: PMC12205896
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-08291-2
Placenta-tropic VEGF mRNA lipid nanoparticles ameliorate murine pre-eclampsia
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Placenta-tropic VEGF mRNA lipid nanoparticles ameliorate murine pre-eclampsia.Nature. 2025 Feb;638(8051):E33. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08605-y. Nature. 2025. PMID: 39900626 No abstract available.
Abstract
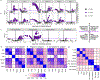
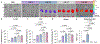
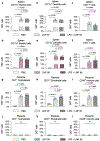
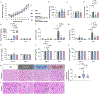
Pre-eclampsia is a placental disorder that affects 3-5% of all pregnancies and is a leading cause of maternal and fetal morbidity worldwide1,2. With no drug available to slow disease progression, engineering ionizable lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for extrahepatic messenger RNA (mRNA) delivery to the placenta is an attractive therapeutic option for pre-eclampsia. Here we use high-throughput screening to evaluate a library of 98 LNP formulations in vivo and identify a placenta-tropic LNP (LNP 55) that mediates more than 100-fold greater mRNA delivery to the placenta in pregnant mice than a formulation based on the Food and Drug Administration-approved Onpattro LNP (DLin-MC3-DMA)3. We propose an endogenous targeting mechanism based on β2-glycoprotein I adsorption that enables LNP delivery to the placenta. In both inflammation- and hypoxia-induced models of pre-eclampsia, a single administration of LNP 55 encapsulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA resolves maternal hypertension until the end of gestation. In addition, with our VEGF mRNA LNP 55 therapeutic, we demonstrate improvements in fetal health and partially restore placental vasculature, the local and systemic immune landscape and serum levels of soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase-1, a clinical biomarker of pre-eclampsia1. Together, these results demonstrate the potential of this mRNA LNP platform for treating placental disorders such as pre-eclampsia.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: K.L.S., H.C.S., H.C.G. and M.J.M. have filed a patent application based on this work. M.J.M. is an inventor on a patent related to this work filed by the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania (PCT/US20/56252). D.W. is an inventor on several patents related to this work filed by the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania (11/990,646; 13/ 585,517; 13/839,023; 13/839,155; 14/456,302; 15/339,363; 16/299,202). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


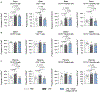

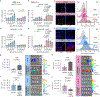
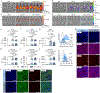

Comment in
-
Lipid nanoparticle ferries therapeutic mRNA to the placenta.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025 Feb;24(2):90. doi: 10.1038/d41573-025-00003-3. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 39775151 No abstract available.
-
Targeting inherited mutations to prevent metastasis.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025 Feb;24(2):90. doi: 10.1038/d41573-025-00009-x. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 39806011 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chappell LC, Cluver CA, Kingdom J & Tong S. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 398, 341–354 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Swingle KL, Ricciardi AS, Peranteau WH & Mitchell MJ Delivery technologies for women’s health applications. Nat. Rev. Bioeng 1, 408–425 (2023).
-
- Adams D. et al. Patisiran, an RNAi therapeutic, for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. New Engl. J. Med 379, 11–21 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

