Comparing the safety and efficacy of remimazolam-based total intravenous anesthesia versus volatile agent-based anesthesia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 39663669
- PMCID: PMC11834889
- DOI: 10.4097/kja.24444
Comparing the safety and efficacy of remimazolam-based total intravenous anesthesia versus volatile agent-based anesthesia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Remimazolam is a novel short-acting benzodiazepine that has recently been used for general anesthesia. This study compared the safety and efficacy of remimazolam-based total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) and volatile agent-based anesthesia in adults undergoing general anesthesia.
Methods: We searched electronic databases including PubMed, Embase, CENTRAL, and Scopus for relevant studies. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who experienced hypotension during surgery. Secondary outcomes included incidence of bradycardia, extubation time, duration in the post-anesthesia care unit hospital stay, and incidence of postoperative nausea and/or vomiting (PONV). We estimated the relative risk (RR) and mean difference with 95% CIs using a random-effects model.
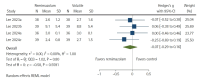
Results: A total of 969 patients from 12 randomized controlled trials were included. The incidence of hypotension was 14% and 34% in the remimazolam and volatile agent groups, respectively. Remimazolam significantly lowered the incidence of hypotension (RR: 0.43, 95% CI [0.29-0.63], P = 0.0000, I2 = 26%). The remimazolam group had a PONV incidence of 13%, compared to 28% in the volatile agent group, indicating a significant difference (RR: 0.51, 95% CI [0.37-0.72], P = 0.0001, I2 = 15%). No significant differences were observed in the other outcomes.
Conclusions: Remimazolam-based TIVA demonstrated favorable hemodynamic effects, with a lower incidence of hypotension and similar bradycardia rates, compared to volatile agent-based anesthesia. Furthermore, the reduction in PONV supports the use of remimazolam-based TIVA as a valuable method for general anesthesia.
Keywords: Anesthesia, general; Anesthesia, inhalation; Anesthesia, intravenous; Postoperative nausea and vomiting; Remimazolam; Safety..
Conflict of interest statement
Jung-Hee Ryu has been an editor for the Korean Journal of Anesthesiology since 2019. However, she was not involved in any process of review for this article, including peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision-making. There were no other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Remimazolam vs. propofol for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of emergence agitation risk in surgical populations.J Clin Anesth. 2025 Apr;103:111815. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2025.111815. Epub 2025 Mar 22. J Clin Anesth. 2025. PMID: 40120546
-
Comparing subjective quality of recovery between remimazolam- and propofol-based total intravenous anesthesia for surgical procedures: a meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2024 Sep 17;13(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02660-8. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39289773 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of remimazolam for general anesthesia on postoperative nausea and vomiting : A systematic review and meta-analysis.Anaesthesiologie. 2024 Oct;73(10):685-693. doi: 10.1007/s00101-024-01454-w. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Anaesthesiologie. 2024. PMID: 39271579 English.
-
Effect of remimazolam on postoperative delirium and cognitive function in adults undergoing general anesthesia or procedural sedation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025 Apr;78(2):118-128. doi: 10.4097/kja.24493. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 39748753 Free PMC article.
-
The incidences of nausea and vomiting after general anesthesia with remimazolam versus sevoflurane: a prospective randomized controlled trial.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2024 Aug;77(4):441-449. doi: 10.4097/kja.23939. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38637272 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Koyama Y, Nishikawa H, Murase Y, Morita K, Tsuzaki K. General anesthesia using remimazolam and remifentanil in combination with local anesthetics without neuromuscular blocking agents in a patient with myotonic dystrophy. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2023;76:391–3. doi: 10.4097/kja.23133. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

