PPAR α affects hepatic lipid homeostasis by perturbing necroptosis signals in the intestinal epithelium
- PMID: 39664413
- PMCID: PMC11628832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.08.021
PPAR α affects hepatic lipid homeostasis by perturbing necroptosis signals in the intestinal epithelium
Abstract
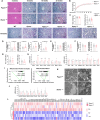
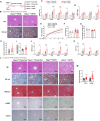
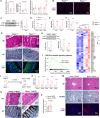
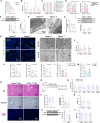
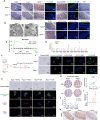
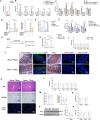
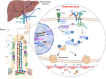
Rapid turnover of the intestinal epithelium is a critical strategy to balance the uptake of nutrients and defend against environmental insults, whereas inappropriate death promotes the spread of inflammation. PPARα is highly expressed in the small intestine and regulates the absorption of dietary lipids. However, as a key mediator of inflammation, the impact of intestinal PPARα signaling on cell death pathways is unknown. Here, we show that Pparα deficiency of intestinal epithelium up-regulates necroptosis signals, disrupts the gut vascular barrier, and promotes LPS translocation into the liver. Intestinal Pparα deficiency drives age-related hepatic steatosis and aggravates hepatic fibrosis induced by a high-fat plus high-sucrose diet (HFHS). PPARα levels correlate with TRIM38 and MLKL in the human ileum. Inhibition of PPARα up-regulates necroptosis signals in the intestinal organoids triggered by TNF-α and LPS stimuli via TRIM38/TRIF and CREB3L3/MLKL pathways. Butyric acid ameliorates hepatic steatosis induced by intestinal Pparα deficiency through the inhibition of necroptosis. Our data suggest that intestinal PPARα is essential for the maintenance of microenvironmental homeostasis and the spread of inflammation via the gut-liver axis.
Keywords: Butyric acid; Gut–liver axis; Intestine; LPS; Liver; NAFLD; Necroptosis; PPARα.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zou Z.Y., Shen B., Fan J.G. Systematic review with meta-analysis: epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2019;25:1764–1772. - PubMed
-
- Bunger M., van den Bosch H.M., van der Meijde J., Kersten S., Hooiveld G.J., Muller M. Genome-wide analysis of PPARalpha activation in murine small intestine. Physiol Genomics. 2007;30:192–204. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

