Politicians, power, and the people's health: US elections and state health outcomes, 2012-2024
- PMID: 39664487
- PMCID: PMC11631342
- DOI: 10.1093/haschl/qxae163
Politicians, power, and the people's health: US elections and state health outcomes, 2012-2024
Abstract
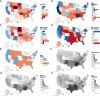
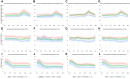
Our descriptive study examined current associations (2022-2024) between US state-level health outcomes and 4 US state-level political metrics: 2 rarely used in public health research (political ideology of elected representatives based on voting records; trifectas, where 1 party controls the executive and legislative branches) and 2 more commonly used (state policies enacted; voter political lean). The 8 health outcomes spanned the life course: infant mortality, premature mortality (death at age <65), health insurance (adults aged 35-64), vaccination for children and persons aged ≥65 (flu; COVID-19 booster), maternity care deserts, and food insecurity. For the first 3 outcomes, we also examined trends in associations (2012-2024). For all political metrics, higher state-level political conservatism was associated with worse health outcomes, especially for the metrics for political ideology and state trifectas. For example, in 2016, the premature mortality rate in states with Republican vs Democratic trifectas was higher by 55.4 deaths per 100 000 person-years (95% CI: 7.7, 103.1), and the slope of the rate of increase to 2021 was also higher, by 27.0 deaths per 100 000 person-years (95% CI: 24.4, 29.7). These results suggest elections, political ideology, and concentrations of political power matter for population health.
Keywords: COVID-19 boosters; childhood vaccination; electoral politics; food insecurity; health insurance; infant mortality; maternity care deserts; political conservatism; political determinants of health; political liberalism; political polarization; poverty; premature mortality; state policies; state trifecta.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Project HOPE - The People-To-People Health Foundation, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest Please see ICMJE form(s) for author conflicts of interest. These have been provided as supplementary materials.
Figures

References
-
- McGuire JW. Democracy and Population Health. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2020.
-
- Fafard P, Cassola A, de Leeuw E. Integrating Science and Politics for Public Health. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International; 2022.
-
- Beckfield J. Political Sociology and the People's Health. New York: Oxford University Press; 2018.
-
- Oberlander J. Polarization, partisanship, and health in the United States. J Health Polit Policy Law. 2024;49(3):329–350. - PubMed
-
- Keena A, Latner M, McGann AJM, Smith CA. Gerrymandering the States: Partisanship, Race, and the Transformation of American Federalism. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2021.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
