Fatty Acid Metabolism Disruptions: A Subtle yet Critical Factor in Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes
- PMID: 39664564
- PMCID: PMC11628336
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.103404
Fatty Acid Metabolism Disruptions: A Subtle yet Critical Factor in Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes
Abstract
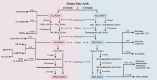
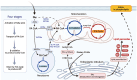
The establishment and maintenance of pregnancy encompass a series of complex and high-energy-consuming physiological processes, resulting in a significant energy demand. Fatty acids, one of the most essential nutrients, play a crucial role in energy supply via oxidation and perform critical biological functions such as anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects, which substantially impact human health. Disordered fatty acid metabolism can cause anomalies in fetal growth and development, as well as a range of pregnancy problems, which can influence the health of both the mother and the fetus. In this review, we innovatively explore the relationship between fatty acid metabolism abnormalities and pregnancy complications, emphasizing the potential of dietary interventions with polyunsaturated fatty acids in improving pregnancy outcomes. These findings provide important evidence for clinical interventions and enhance the understanding and practical application of health management during pregnancy.
Keywords: fatty acid oxidation; inflammation; omega-3 fatty acids; oxidative stress; pregnancy outcomes.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Dunning KR, Robker RL. Promoting lipid utilization with l-carnitine to improve oocyte quality. Anim Reprod Sci. 2012;134:69–75. - PubMed
-
- Oey NA, Ruiter JP, Attie-Bitach T, Ijlst L, Wanders RJ, Wijburg FA. Fatty acid oxidation in the human fetus: implications for fetal and adult disease. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2006;29:71–5. - PubMed
-
- Shekhawat P, Bennett MJ, Sadovsky Y, Nelson DM, Rakheja D, Strauss AW. Human placenta metabolizes fatty acids: implications for fetal fatty acid oxidation disorders and maternal liver diseases. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003;284:E1098–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

