How PPAR-alpha mediated inflammation may affect the pathophysiology of chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 39665027
- PMCID: PMC11629568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphys.2024.100133
How PPAR-alpha mediated inflammation may affect the pathophysiology of chronic kidney disease
Abstract
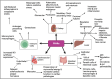
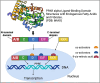
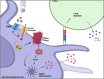
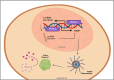
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major risk factor for death in adults. Inflammation plays a role in the pathogenesis of CKD, but the mechanisms are poorly understood. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α) is a nuclear receptor and one of the three members (PPARα, PPARβ/δ, and PPARγ) of the PPARs that plays an important role in ameliorating pathological processes that accelerate acute and chronic kidney disease. Although other PPARs members are well studied, the role of PPAR-α is not well described and its role in inflammation-mediated chronic disease is not clear. Herein, we review the role of PPAR-α in chronic kidney disease with implications for the immune system.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Immunity; Inflammation; PPAR-α; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Afsar B., et al. Salt intake and immunity. Hypertension. 2018;72(1):19–23. - PubMed
-
- Ahadzadeh E., et al. The chemokine receptor CX(3)CR1 reduces renal injury in mice with angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018;315(6):F1526–f1535. - PubMed
-
- Akchurin O.M., Kaskel F. Update on inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2015;39(1–3):84–92. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

