Exploring the Fecal Metabolome in Infants With Cow's Milk Allergy: The Distinct Impacts of Cow's Milk Protein Tolerance Acquisition and of Synbiotic Supplementation
- PMID: 39665335
- PMCID: PMC11704826
- DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.202400583
Exploring the Fecal Metabolome in Infants With Cow's Milk Allergy: The Distinct Impacts of Cow's Milk Protein Tolerance Acquisition and of Synbiotic Supplementation
Abstract
Scope: Cow's milk allergy (CMA) is one of the most prevalent food allergies in early childhood, often treated via elimination diets including standard amino acid-based formula or amino acid-based formula supplemented with synbiotics (AAF or AAF-S). This work aimed to assess the effect of cow's milk (CM) tolerance acquisition and synbiotic (inulin, oligofructose, Bifidobacterium breve M-16 V) supplementation on the fecal metabolome in infants with IgE-mediated CMA.
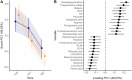
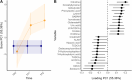
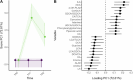
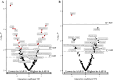
Methods and results: The CMA-allergic infants received AAF or AAF-S for a year during which fecal samples were collected. The samples were subjected to metabolomics analyses covering gut microbial metabolites including SCFAs, tryptophan metabolites, and bile acids (BAs). Longitudinal data analysis suggested amino acids, BAs, and branched SCFAs alterations in infants who outgrew CMA during the intervention. Synbiotic supplementation significantly modified the fecal metabolome after 6 months of intervention, including altered purine, BA, and unsaturated fatty acid levels, and increased metabolites of infant-type Bifidobacterium species: indolelactic acid and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid.
Conclusion: This study offers no clear conclusion on the impact of CM-tolerance acquisition on the fecal metabolome. However, our results show that 6 months of synbiotic supplementation successfully altered fecal metabolome and suggest induced bifidobacteria activity, which subsequently declined after 12 months of intervention.
Keywords: bifidobacteria; early life; food allergy; fructooligosaccharides; metabolomics.
© 2024 The Author(s). Molecular Nutrition & Food Research published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Harm Wopereis is an employee of Danone Research & Innovation. The project is part of a partnership program between NWO‐TTW and Danone Research & Innovation. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sicherer S. H. and Sampson H. A., “Food Allergy,” Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 125 (2010): S116–S125. - PubMed
-
- Høst A., “Frequency of Cow's Milk Allergy in Childhood,” Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology 89 (2002): 33–37. - PubMed
-
- Schoemaker A. A., Sprikkelman A. B., Grimshaw K. E., et al., “Incidence and Natural History of Challenge‐Proven Cow's Milk Allergy in European Children—EuroPrevall Birth Cohort,” Allergy 70 (2015): 963–972. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

