Digital Pathology-based Artificial Intelligence Biomarker Validation in Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 39665917
- PMCID: PMC12369405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euo.2024.11.009
Digital Pathology-based Artificial Intelligence Biomarker Validation in Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Background and objective: Owing to the expansion of treatment options for metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC) and an appreciation of clinical subgroups with differential prognosis and treatment responses, prognostic and predictive biomarkers are needed to personalize care in this setting. Our aim was to evaluate a multimodal artificial intelligence (MMAI) biomarker for prognostic ability in mHSPC.
Methods: We used data from the phase 3 CHAARTED trial; 456/790 patients with mHSPC had evaluable digital histopathology images and requisite clinical variables to generate MMAI scores for inclusion in our analysis. We assessed the association of MMAI score with overall survival (OS), clinical progression (CP), and castration-resistant PC (CRPC) via univariable Cox proportional-hazards and Fine-Gray models.
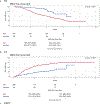
Key findings and limitations: In the analysis cohort, 370 patients (81.1%) were classified as MMAI-high and 86 (18.9%) as MMAI-intermediate/low risk. Estimated 5-yr OS was 39% for the MMAI-high, 58% for the MMAI-intermediate, and 83% for the MMAI-low groups (log-rank p < 0.001). The MMAI score was associated with OS (hazard ratio [HR] 1.51, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.33-1.73; p < 0.001), CP (subdistribution HR 1.54, 95% CI 1.36-1.74; p < 0.001), and CRPC (subdistribution HR 1.63, 95% CI 1.45-1.83; p < 0.001). The proportion of MMAI-high cases was 50.0%, 83.7%, 66.7%, and 92.1% in the subgroups with low-volume metachronous (n = 74), low-volume synchronous (n = 80), high-volume metachronous (n = 48), and high-volume synchronous (n = 254) mHSPC, respectively. The MMAI biomarker remained prognostic after adjustment for treatment, volume status, and diagnosis stage.
Conclusions and clinical implications: Our findings show that the MMAI biomarker is prognostic for OS, CP, and CRPC among patients with mHSPC, regardless of clinical subgroup or treatment received. Further investigations of MMAI biomarkers in advanced PC are warranted.
Patient summary: We looked at the performance of an artificial intelligence (AI) tool that interprets images of samples of prostate cancer tissue in a group of men whose cancer had spread beyond the prostate. The AI tool was able to identify patients at higher risk of worse outcomes. These results show the potential benefit of AI tools in helping patients and their health care team in making treatment decisions.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Biomarker; Digital pathology; Prognosis; Prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2024 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosures
Dr. Markowski reported consulting roles to Clovis Oncology and Exelexis. Dr Parker is a current employee of University College London (UCL); Artera has a financial relationship with University College London (UCL) as part of a data licensing agreement from which UCL may benefit financially. Mr. Ren, Dr. Tierney, Dr. Royce, Dr. Yamashita, Dr. Croucher, Ms. Huang, Ms. Todorovic, Dr. Chen, and Dr. Showalter are current employees with equity interest in Artera Inc. Dr. Esteva is a co-founder and CEO of Artera Inc. Dr. Feng is an advisor with equity interest to Artera Inc. Dr. Sweeney reported institutional research funding from Janssen, Astellas, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Bayer; patents, consulting, or an advisory role with Sanofi, Johnson and Johnson, Astellas, Bayer, Genentech/Roche, Pfizer, Lilly, CellCentric, PointBiopharma, Amphista, QEDDI, and BMS; royalties and other intellectual property from Parthenolide (Indiana University), dimethylamino parthenolide (Leuchemix), Exelixis: Abiraterone plus cabozantinib combination, FRAS1 SNP and tristetraprolin as biomarkers of lethal prostate cancer; and stock or other ownership interest in Leuchemix. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous