How to deal with frenemy NRF2: Targeting NRF2 for chemoprevention and cancer therapy
- PMID: 39666284
- PMCID: PMC10629913
- DOI: 10.38212/2224-6614.3463
How to deal with frenemy NRF2: Targeting NRF2 for chemoprevention and cancer therapy
Abstract
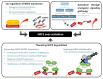
Induction of antioxidant proteins and phase 2 detoxifying enzymes that neutralize reactive electrophiles are important mechanisms for protection against carcinogenesis. Normal cells provide multifaceted pathways to tightly control NF-E2-related factor 2 (NRF2)-mediated gene expression in response to an assault by a range of endogenous and exogenous oncogenic molecules. Transient activation of NRF2 by its activators is able to induce ARE-mediated cytoprotective proteins which are essential for protection against various toxic and oxidative damages, and NRF2 activators thereby have efficacy in cancer chemoprevention. Because NRF2 has a cytoprotective function, it can protect normal cells from carcinogens like an angel, but when the protective effect acts on cancer cells, it will give rise to invincible cancer cells and play a devilish role in tumor progression. Indeed, aberrant activation of NRF2 has been found in a variety of cancers that create a favorable environment for the proliferation and survival of cancer cells and leads to drug resistance, ultimately leading to the poor clinical prognosis of patients. Therefore, pharmacological inhibition of NRF2 signaling has emerged as a promising approach for cancer therapy. This review aims to compile the regulatory mechanisms of NRF2 and its double-edged role in cancer. In addition, we also summarize the research progress of NRF2 modulators, especially phytochemicals, in chemoprevention and cancer therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Menegon S, Columbano A, Giordano S. The dual roles of NRF2 in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2016;22:578–93. - PubMed
-
- Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Katoh Y, et al. An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;236:313–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical