Dual role of neuroplastin in pancreatic β cells: Regulating insulin secretion and promoting islet inflammation
- PMID: 39666939
- PMCID: PMC11331099
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2411234121
Dual role of neuroplastin in pancreatic β cells: Regulating insulin secretion and promoting islet inflammation
Abstract
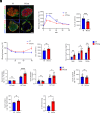
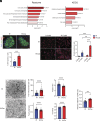
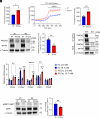
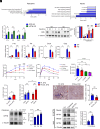
Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident secretory protein that reduces inflammation and promotes proliferation in pancreatic β cells. Numerous studies have highlighted the potential of MANF as a therapeutic agent for diabetes mellitus (DM), making it essential to understand the mechanisms underlying MANF's functions. In our previous search for a molecule that mediates MANF signaling, we identified Neuroplastin (NPTN) as a binding partner of MANF that localizes on the cell surface. However, the roles of NPTN in pancreatic β cells remain unclear. In this study, we generated β cell-specific Nptn knockout (KO) mice and conducted metabolic characterization. NPTN deficiency improved glucose tolerance by increasing insulin secretion and β cell mass in the pancreas. Moreover, proliferation and mitochondrial numbers in β cells increased in Nptn KO islets. These phenotypes resulted from elevated cytosolic Ca2+ levels and subsequent activation of downstream molecules. Simultaneously, we demonstrated that NPTN induces the expression of proinflammatory cytokines via the TRAF6-NF-κB axis in β cells. Additionally, NPTN deficiency conferred resistance to streptozotocin-induced diabetic phenotypes. Finally, exogenous MANF treatment in islets or β cells led to similar phenotypes as those observed in NPTN-deficient models. These results indicate that NPTN plays important roles in the regulation of insulin secretion, proliferation, and mitochondrial quantity, as well as proinflammatory responses, which are antagonized by MANF treatment. Thus, targeting the MANF-NPTN interaction may lead to a novel treatment for improving β cell functions in DM.
Keywords: diabetes; endoplasmic reticulum; β cell.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:F.U. is a Founder and President of CURE4WOLFRAM, Inc., and a Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board for Emerald Biotherapeutcs, Inc. F.U. is an inventor of three patents related to the treatment of Wolfram Syndrome, US 9,891,231 Soluble Manf in Pancreatic Beta Cell Disorders and US 10,441,574 and US 10,695,324 Treatment for Wolfram Syndrome and Other ER Stress Disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Lindahl M., Saarma M., Lindholm P., Unconventional neurotrophic factors CDNF and MANF: Structure, physiological functions and therapeutic potential. Neurobiol. Dis. 97, 90–102 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Tang Q., Li Y., He J., MANF: An emerging therapeutic target for metabolic diseases. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 33, 236–246 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

