Polysulfide and persulfide-mediated activation of the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway increases Sestrin2 expression and reduces methylglyoxal toxicity
- PMID: 39667306
- PMCID: PMC11697784
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103450
Polysulfide and persulfide-mediated activation of the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway increases Sestrin2 expression and reduces methylglyoxal toxicity
Abstract
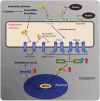
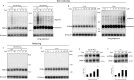
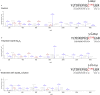
Unfolded protein response (UPR) is activated in cells under endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. One sensor protein involved in this response is PERK, which is activated through its redox-dependent oligomerization. Prolonged UPR activation is associated with the development and progression of various diseases, making it essential to understanding the redox regulation of PERK. Sulfane sulfur, such as polysulfides and persulfides, can modify the cysteine residues and regulate the function of various proteins. However, the regulatory mechanism and physiological effects of sulfane sulfur on the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway remain poorly understood. This study focuses on the persulfidation of PERK to elucidate the effects of polysulfides on the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway and investigate its cytoprotective mechanism. Here, we demonstrated that polysulfide treatment promoted the oligomerization of PERK and PTP1B in neuronal cells using western blotting under nonreducing conditions. We also observed that l-cysteine, a biological source of sulfane sulfur, promoted the oligomerization of PERK and the knockdown of CBS and 3-MST, two sulfane sulfur-producing enzymes, and reduced PERK oligomerization induced by l-cysteine treatment. Furthermore, the band shift assay and LC-MS/MS studies revealed that polysulfides and persulfides induce PTP1B and PERK persulfidation. Additionally, polysulfides promoted eIF2α phosphorylation and ATF4 accumulation in the nucleus, suggesting that polysulfides activate the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway in neuronal cells. Moreover, polysulfides protected neuronal cells from methylglyoxal-induced toxicity, and this protective effect was reduced when the expression of Sestrin2, regulated by ATF4 activity, was suppressed. This study identified a novel mechanism for the activation of the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway through persulfidation by polysulfides and persulfides. Interestingly, activation of this pathway overcame the toxicity of methylglyoxal in dependence on Sestrin2 expression. These findings deepen our understanding of neuronal diseases involving ER stress and UPR disturbance and may inspire new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Methylglyoxal; Persulfide; Polysulfide; Sestrin2; UPR pathway.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors claim no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress response mediated by the PERK-eIF2(alpha)-ATF4 pathway is involved in osteoblast differentiation induced by BMP2.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 11;286(6):4809-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.152900. Epub 2010 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21135100 Free PMC article.
-
PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress response is involved in osteodifferentiation of human periodontal ligament cells under cyclic mechanical force.Cell Signal. 2016 Aug;28(8):880-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 27079961
-
Melatonin Induces PERK-ATF4 Unfolded Protein Response and Apoptosis in Human Choriocarcinoma Cells.J Pineal Res. 2025 Sep;77(5):e70072. doi: 10.1111/jpi.70072. J Pineal Res. 2025. PMID: 40873119 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP Signaling Pathway in Tumor Progression During Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Curr Mol Med. 2016;16(6):533-44. doi: 10.2174/1566524016666160523143937. Curr Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27211800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4 module of the UPR in hypoxia resistance and tumor growth.Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Jul;5(7):723-8. doi: 10.4161/cbt.5.7.2967. Epub 2006 Jul 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16861899 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of redox signaling in mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum regulation in kidney diseases.Arch Toxicol. 2025 May;99(5):1865-1891. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-04041-z. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40214774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondria-Nuclear Crosstalk: Orchestrating mtDNA Maintenance.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2025 Jun;66(5):222-242. doi: 10.1002/em.70013. Epub 2025 May 26. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2025. PMID: 40418056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bertolotti A., Zhang Y., Hendershot L.M., Harding H.P., Ron D. Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000;2:326–332. - PubMed
-
- Harding H.P., Zhang Y., Ron D. Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature. 1999;397:271–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

