Synthesis of eco-friendly lipid-magnetite nanocomposite encapsulated Poinciana extract as promising insecticide against Culex pipiens
- PMID: 39668148
- PMCID: PMC11638267
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81078-7
Synthesis of eco-friendly lipid-magnetite nanocomposite encapsulated Poinciana extract as promising insecticide against Culex pipiens
Abstract
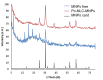
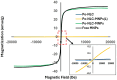
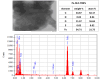
Mosquito-borne diseases represent a growing health challenge over time. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) are the second generation of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), and they continue to attract significant interest as potential diagnostic and therapeutic tools in disease inhibition and insect control. Activated ingredients presented in the Poinciana leaves were extracted and GC-MS data indicated an increased abundance of terpenes, flavonoids, and phenolic substances. Poinciana extract was encapsulated to the vicinity of nanostructure lipid carrier, Po-NLC, and surface modified with magnetic nanoparticles, Po-NLC-MNPs. The synthesized nanoparticles depicted average particle size of 73.2 and 75.55 nm while zeta potential of (- 29.4) and (‒ 4.44 mV) for Po-NLC and Po-NLC-MNPs, respectively. Transmission electron microscope and morphology determination showed regular, irregular spherical and oval shapes with diverse single particle size. X-rays diffraction pattern of the freely synthesized MNPs was compared to the decorated NLC and the results manifested that the NLC was successfully decorated with MNPs. The larvicidal activity of plant extract, Poinciana extract (Po), and their nanoparticle conjugates against 3rd instar larvae of Culex pipiens was evaluated at 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, and 1500 ppm concentrations. Both high and low concentrations of Po-NLC-MNPs, indicated potential larval mortality than plant extracts (Po extract) itself. The mortality rate reached 100% for 3rd instar larvae. Based on their relative toxicity, (Po-NLC-MNPs) was the best at killing larvae, followed by Po-NLC. The synthesized nps were checked for their cytotoxic effect against wi38 cell line. The in-vitro cytotoxicity results indicated that there was no significant cytotoxicity and the nanocomposite barely caused weak changes in the tested cells. The synthesized nanoparticles have potential to create a new generation of eco-friendly, effective alternatives for controlling mosquito-borne diseases.
Keywords: Culex pipiens; Poinciana extract; Nanostructured lipid carriers; Phytochemical analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Evaluating larvicidal, ovicidal and growth inhibiting activity of five medicinal plant extracts on Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae), the West Nile virus vector.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 23;14(1):19660. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69449-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39191818 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the impact of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in relation to malaria and filariasis vector control against Anopheles stephensi Liston and Culex quinquefasciatus Say (Diptera: Culicidae).Parasitol Res. 2013 Feb;112(2):487-99. doi: 10.1007/s00436-012-3158-5. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Parasitol Res. 2013. PMID: 23064800
-
Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) for Biologically Active Green Tea and Fennel Natural Oils Delivery: Larvicidal and Adulticidal Activities against Culex pipiens.Molecules. 2022 Mar 17;27(6):1939. doi: 10.3390/molecules27061939. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35335302 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of eco-friendly silver nanoparticles from Morinda tinctoria leaf extract and its larvicidal activity against Culex quinquefasciatus.Parasitol Res. 2015 Feb;114(2):411-7. doi: 10.1007/s00436-014-4198-9. Epub 2014 Nov 7. Parasitol Res. 2015. PMID: 25373452
-
Spectral and HRTEM analyses of Annona muricata leaf extract mediated silver nanoparticles and its Larvicidal efficacy against three mosquito vectors Anopheles stephensi, Culex quinquefasciatus, and Aedes aegypti.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2015 Dec;153:184-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.09.018. Epub 2015 Sep 21. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2015. PMID: 26410042
Cited by
-
Nanoencapsulation enhances stability, release behavior, and antimicrobial properties of Sage and Thyme essential oils.Sci Rep. 2025 May 26;15(1):18373. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00022-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40419505 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity of Foeniculum vulgare essential oil, its main component and nanoformulation against Phthorimaea absoluta and the generalist predator Macrolophus pygmaeus.Sci Rep. 2025 May 14;15(1):16706. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01193-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40369160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coetzee, M. Vol. 108 179–180 (Oxford University Press, 2014).
-
- WHO. (World Health Organization Washington, 2014).
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

