African ancestry neurodegeneration risk variant disrupts an intronic branchpoint in GBA1
- PMID: 39668204
- PMCID: PMC11638064
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01423-2
African ancestry neurodegeneration risk variant disrupts an intronic branchpoint in GBA1
Abstract
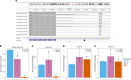
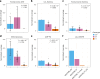
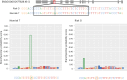
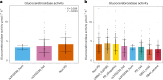
Recently, an African ancestry-specific Parkinson disease (PD) risk signal was identified at the gene encoding glucocerebrosidase (GBA1). This variant ( rs3115534 -G) is carried by ~50% of West African PD cases and imparts a dose-dependent increase in risk for disease. The risk variant has varied frequencies across African ancestry groups but is almost absent in European and Asian ancestry populations. GBA1 is a gene of high clinical and therapeutic interest. Damaging biallelic protein-coding variants cause Gaucher disease and monoallelic variants confer risk for PD and dementia with Lewy bodies, likely by reducing the function of glucocerebrosidase. Interestingly, the African ancestry-specific GBA1 risk variant is a noncoding variant, suggesting a different mechanism of action. Using full-length RNA transcript sequencing, we identified partial intron 8 expression in risk variant carriers (G) but not in nonvariant carriers (T). Antibodies targeting the N terminus of glucocerebrosidase showed that this intron-retained isoform is likely not protein coding and subsequent proteomics did not identify a shorter protein isoform, suggesting that the disease mechanism is RNA based. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats editing of the reported index variant ( rs3115534 ) revealed that this is the sequence alteration responsible for driving the production of these transcripts containing intron 8. Follow-up analysis of this variant showed that it is in a key intronic branchpoint sequence and, therefore, has important implications in splicing and disease. In addition, when measuring glucocerebrosidase activity, we identified a dose-dependent reduction in risk variant carriers. Overall, we report the functional effect of a GBA1 noncoding risk variant, which acts by interfering with the splicing of functional GBA1 transcripts, resulting in reduced protein levels and reduced glucocerebrosidase activity. This understanding reveals a potential therapeutic target in an underserved and underrepresented population.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: M.M.B’s, H.L.’s and M.A.N.’s participation in this project was part of a competitive contract awarded to Data Tecnica International by the NIH to support open science research. M.A.N. also currently serves on the scientific advisory board for Character Bio and is a scientific founder at Neuron23. M.R., S.F., C. Beetz and P.B. are employees of Centogene. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
African ancestry neurodegeneration risk variant disrupts an intronic branchpoint in GBA1.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 24:2024.02.20.24302827. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.20.24302827. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Dec;31(12):1955-1963. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01423-2. PMID: 39802803 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 ES015794/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201600032C/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AG000542/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- ZIC MH002903/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK108803/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG008956/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL138626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG008901/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AG000543/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM127473/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009080/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM136426/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 MD006902/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R56 MD013312/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AG000538/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

