EGFR-V834L combined with L858R mutation reduced afatinib sensitivity and associated to early recurrence in lung cancer
- PMID: 39670006
- PMCID: PMC11632430
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-24-471
EGFR-V834L combined with L858R mutation reduced afatinib sensitivity and associated to early recurrence in lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) osimertinib is widely used as a first-line treatment for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, there is no established treatment for osimertinib resistance, so second-generation afatinib is an alternative treatment option. The purpose of this study was to elucidate gene alterations associated with afatinib efficacy and resistance by analyzing cell-free DNA (cfDNA) obtained from patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
Methods: This study was conducted as a prospective clinical trial in patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC at multiple institutions. We analyzed plasma cfDNA from the patients treated with afatinib as the first-line therapy.
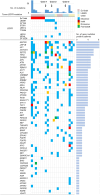
Results: Paired specimens were obtained before and at the time of resistance to afatinib treatment, and specimens only at afatinib resistance were obtained from 22 and 18 patients, respectively. In plasma cfDNA from the 22 cases, driver EGFR mutations were detected in 13 cases (59.1%), and the compound V834L mutation was detected in two cases in cis with EGFR-L858R mutation. The median progression-free survival (mPFS) was remarkably shorter in patients with V834L than in all 22 cases (4.2 vs. 9.2 months). Moreover, we detected V834L and T790M combined with EGFR-L858R in the cfDNA from one patient resistant to afatinib. Preclinical experiments using EGFR-L858R, with or without V834L, in Ba/F3 cells revealed that V834L with L858R conferred resistance to low concentrations of EGFR-TKIs, including afatinib and osimertinib. In three cases of EGFR-L858R+V834L, other co-mutations, including TP53, CTNNB1, and RB1, were detected either before or after afatinib resistance.
Conclusions: These results suggested that V834L cooperates with other coexisting mutations to influence the therapeutic efficacy of EGFR-TKIs.
Keywords: Co-mutation; cell-free DNA (cfDNA); epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI); liquid biopsy; resistance.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-24-471/coif). Tadaaki Yamada serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Translational Lung Cancer Research from October 2023 to September 2025. S.Y. obtained research grants from Chugai-Roche, AstraZeneca and Boehringer-Ingelheim, and speaking honoraria from Chugai-Roche, AstraZeneca and Boehringer-Ingelheim. Tadaaki Yamada obtained research grants from Ono Pharmaceutical, Janssen Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, and speaking honoraria from Eli Lilly, and Chugai-Roche. K.T. obtained research grants from Taiho Pharmaceutical, and speaking honoraria from Astrazeneca, Chugai-Roche, Eli-Lilly, MSD, Daiichi-Sankyo, Boehringer-Ingelheim and Ono Pharamaceutical. K.S. obtained speaking honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Chugai-Roche. Y.T. obtained research grants from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, MSD, Beigene, and Regeneron. K.K. obtained research grants from Boehringer-Ingelheim. S.K. obtained research grants from Boehringer-Ingelheim. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:239-46. 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
