Characterization of the BH1406 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell line carrying an activating SOS1 mutation
- PMID: 39670010
- PMCID: PMC11632420
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-24-570
Characterization of the BH1406 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell line carrying an activating SOS1 mutation
Abstract
Background: Approximately 30% of the non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients which harbor no recognizable oncogenic driver mutation are not eligible for targeted therapy. Functional drug screening of tumor cells helps to identify susceptible drug targets not recognized by gene panels for targeted mutation analysis. The aim of this study is to characterize the BH1406 cell line carrying an activating SOS1 mutation and to check its sensitivity to cognate inhibitors.
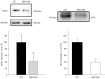
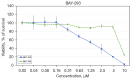
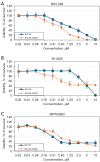
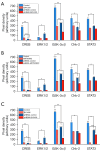
Methods: The NSCLC cell line BH1406 was established from a pleural effusion and found to be sensitive to the SOS1 inhibitor BAY-293 in initial viability screenings. Since in a limited next-generation sequencing (NGS) lung cancer mutation panel no driver could be detected, the patient underwent chemotherapy with poor outcome. This cell line was further characterized by exome sequencing, SOS1 Western blotting, comparison of two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) chemosensitivity assays and phosphoprotein arrays.
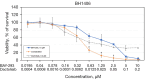
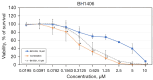
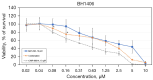
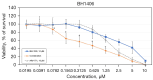
Results: In whole-exome sequencing (WES) the SOS1 mutation P481delinsLFFL, positioned near the known P478L activating mutation was detected. Besides BAY-293, BH1406 cells proved to be sensitive to the SOS1 inhibitors MRTX0902 and BI-3406. The sensitivity of BH1406 cells to BI-3406 was increased under 3D conditions compared to 2D cultures. Western blot phosphoprotein arrays revealed reduced phosphorylation of CREB, GSK3, CHK-2 and STAT3 in BH1406 by BAY-293 treatment in 2D culture. In 3D conditions, cells switched from GSK3α to elevated ERK1/2 signaling, again blocked by the SOS1 inhibitor BAY-293. Similar results were obtained for the SOS1 inhibitors MRTX0902 and BI3406. Additionally, the PI3K inhibitor dactolisib, the GSK-3 inhibitor BI-5521 as well as the bromodomain protein-directed PROTAC ARV-771 inhibited the growth of BH1406 cells significantly and showed synergistic interaction with BAY-293. Furthermore, Western blots demonstrated reduced expression of SOS1 and MYC proteins in response to BAY-293 treatment.
Conclusions: The rare SOS1 P481delinsLFFL mutation in lung cancer may be targetable with corresponding inhibitors, alone or in combination with GSK3/PI3K/BET inhibitors. BH1406 cells represent a novel cellular model suitable for the molecular characterization of SOS1 druggability. Such rare oncogenic driver genes are not included in standard NGS panels and need to be detected by expanded assays like WES.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); SOS1; SOS1 inhibitors; cell signaling; mutation.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-24-570/coif). G.H. serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Translational Lung Cancer Research from September 2023 to August 2025. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
