Multimodal Pilot Evaluation of a Hyaluronic Acid Infraorbital Filler Using Precise, Multipositional, 3-Dimensional Imaging Quantification, Patient-Reported Outcomes, and Anatomic Cadaveric Assessments
- PMID: 39670215
- PMCID: PMC11635449
- DOI: 10.1093/asjof/ojae086
Multimodal Pilot Evaluation of a Hyaluronic Acid Infraorbital Filler Using Precise, Multipositional, 3-Dimensional Imaging Quantification, Patient-Reported Outcomes, and Anatomic Cadaveric Assessments
Abstract
Background: Despite the high demand of filler in the infraorbital area, there remains debate on injection practices, precise anatomical placement, and hyaluronic acid (HA) filler behavior.
Objectives: We aimed to contribute to the clinical and anatomic understanding of infraorbital HA injection through a prospective patient injection study in combination with a cadaveric analysis.
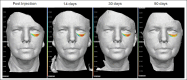
Methods: Patients were injected with Volbella XC (JUVÉDERM, Allergan Aesthetics, an AbbVie Company, Irvine, CA) into the tear trough region by a single experienced aesthetic plastic surgeon. Over a 90-day period, precise undereye volumetric measurements using 3-dimensional photogrammetry (VECTRA-M3, Canfield Scientific, Inc., Fairfield, NJ) and patient-reported outcomes (PROs; FACE-Q) were collected and analyzed relative to 2 pretreatment severity scales. Juvéderm Vycross (Allergan Aesthetics, an AbbVie Company, Irvine, CA) and Restylane NASHA (Galderma, Lausanne, Switzerland) products were injected into the infraorbital and malar region in 6 cephalus specimens and evaluated with regards to the anatomic injection location with and without common clinical physical manipulations.
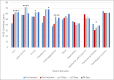
Results: Eleven patients participated with a 100% retention rate. Infraorbital HA volume maintenance was 70% to 81% at 30 days and 50% to 70% at 90 days. Significant improvement was noted in the eyes, overall facial appearance, and cheekbones (P < .05) with FACE-Q outcomes, irrespective of pretreatment severity. In the cadaver examination, we observed differences in the anatomic locations occupied by Juvéderm and Restylane products as well as in behavior after physical manipulation between gel types.
Conclusions: Volbella XC effectively augments undereye volume to diminish infraorbital hollowing as measured over a 90-day period with significantly improved PROs. Enhanced knowledge of the behavior of Volbella XC and other HA fillers in this sensitive anatomic region will lead to improved patient outcomes.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Aesthetic Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Volbella (VYC-15L) for Infraorbital Hollowing: Patient-Reported Outcomes From a Prospective, Multicenter, Single-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Study.Aesthet Surg J. 2023 Oct 13;43(11):1357-1366. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjad100. Aesthet Surg J. 2023. PMID: 37066828 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Novel Use of a Volumizing Hyaluronic Acid Filler for Treatment of Infraorbital Hollows.JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2018 Sep 1;20(5):367-372. doi: 10.1001/jamafacial.2018.0230. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2018. PMID: 29621374 Free PMC article.
-
Visual, Ultrasonographic, and Microscopic Study on Hyaluronic Acid-Based Gel.J Drugs Dermatol. 2016 Sep 1;15(9):1092-8. J Drugs Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27602971
-
Hyaluronic acid gel (Juvéderm) preparations in the treatment of facial wrinkles and folds.Clin Interv Aging. 2008;3(4):629-34. doi: 10.2147/cia.s3118. Clin Interv Aging. 2008. PMID: 19281055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Retrospective Review of the Safety and Efficacy of Low-dose Triamcinolone Mixed with Hyaluronic Acid Fillers to Reduce Post-injection Infraorbital Swelling.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Apr;15(4):13-19. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35465031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons . Plastic Surgery National Statistics. Accessed October 8, 2023. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2022/plastic-su.... 2022.
-
- Filler for wrinkles | JUVÉDERM® . JUVÉDERM®. Accessed October 8, 2023. https://www.juvederm.com/treatment/juvederm-xc
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
