Amygdala intercalated cells form an evolutionarily conserved system orchestrating brain networks
- PMID: 39672964
- PMCID: PMC12318446
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01836-8
Amygdala intercalated cells form an evolutionarily conserved system orchestrating brain networks
Abstract
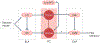
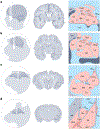
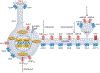
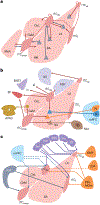
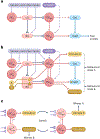
The amygdala attributes valence and emotional salience to environmental stimuli and regulates how these stimuli affect behavior. Within the amygdala, a distinct class of evolutionarily conserved neurons form the intercalated cell (ITC) clusters, mainly located around the boundaries of the lateral and basal nuclei. Here, we review the anatomical, physiological and molecular characteristics of ITCs, and detail the organization of ITC clusters and their connectivity with one another and other brain regions. We describe how ITCs undergo experience-dependent plasticity and discuss emerging evidence demonstrating how ITCs are innervated and functionally regulated by neuromodulatory systems. We summarize recent findings showing that experience alters the balance of activity between different ITC clusters, thereby determining prevailing behavioral output. Finally, we propose a model in which ITCs form a key system for integrating divergent inputs and orchestrating brain-wide circuits to generate behavioral states attuned to current environmental circumstances and internal needs.
© 2024. Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Peripuberty Is a Sensitive Period for Prefrontal Parvalbumin Interneuron Activity to Impact Adult Cognitive Flexibility.Dev Neurosci. 2025;47(2):127-138. doi: 10.1159/000539584. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Dev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 38830346 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical Granularity Shapes the Organization of Afferent Paths to the Amygdala and Its Striatal Targets in Nonhuman Primate.J Neurosci. 2022 Feb 23;42(8):1436-1453. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0970-21.2021. Epub 2021 Dec 28. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34965977 Free PMC article.
-
Fabricating mice and dementia: opening up relations in multi-species research.In: Jenkins N, Jack-Waugh A, Ritchie L, editors. Multi-Species Dementia Studies. Bristol (UK): Bristol University Press; 2025 Feb 25. Chapter 2. In: Jenkins N, Jack-Waugh A, Ritchie L, editors. Multi-Species Dementia Studies. Bristol (UK): Bristol University Press; 2025 Feb 25. Chapter 2. PMID: 40690569 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
References
-
- Grundemann J & Luthi A Ensemble coding in amygdala circuits for associative learning. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol 35, 200–206 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Crosby EC & Humphrey T Studies of the vertebrate telencephalon. II. The nuclear pattern of the anterior olfactory nucleus, tuberculum olfactorium and the amygdaloid complex in adult man. J. Comp. Neurol 74, 309–352 (1941).
-
- Millhouse OE The intercalated cells of the amygdala. J. Comp. Neurol 247, 246–271 (1986). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

