Radiomics and radiogenomics: extracting more information from medical images for the diagnosis and prognostic prediction of ovarian cancer
- PMID: 39673071
- PMCID: PMC11645790
- DOI: 10.1186/s40779-024-00580-1
Radiomics and radiogenomics: extracting more information from medical images for the diagnosis and prognostic prediction of ovarian cancer
Abstract
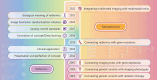
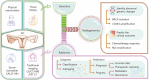
Ovarian cancer (OC) remains one of the most lethal gynecological malignancies globally. Despite the implementation of various medical imaging approaches for OC screening, achieving accurate differential diagnosis of ovarian tumors continues to pose significant challenges due to variability in image performance, resulting in a lack of objectivity that relies heavily on the expertise of medical professionals. This challenge can be addressed through the emergence and advancement of radiomics, which enables high-throughput extraction of valuable information from conventional medical images. Furthermore, radiomics can integrate with genomics, a novel approach termed radiogenomics, which allows for a more comprehensive, precise, and personalized assessment of tumor biological features. In this review, we present an extensive overview of the application of radiomics and radiogenomics in diagnosing and predicting ovarian tumors. The findings indicate that artificial intelligence methods based on imaging can accurately differentiate between benign and malignant ovarian tumors, as well as classify their subtypes. Moreover, these methods are effective in forecasting survival rates, treatment outcomes, metastasis risk, and recurrence for patients with OC. It is anticipated that these advancements will function as decision-support tools for managing OC while contributing to the advancement of precision medicine.
Keywords: Deep learning; Machine learning; Ovarian cancer; Radiogenomics; Radiomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

