Pharmacokinetic study of polymyxin B in healthy subjects and subjects with renal insufficiency
- PMID: 39673151
- PMCID: PMC11645446
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.70110
Pharmacokinetic study of polymyxin B in healthy subjects and subjects with renal insufficiency
Abstract
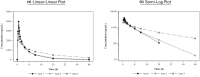
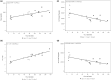
Polymyxin B is a viable option for treating antibiotic-resistant infections; however, current data on its pharmacokinetics, particularly in patients with renal insufficiency, remain inconclusive and necessitates further investigation. To address this gap, we conducted an open-label, single-center, single-dose, parallel-group pharmacokinetic study. Participants received an intravenous dose of 0.75 mg/kg of polymyxin B and were categorized based on their renal function: those with normal function (creatinine clearance [CLcr] ≥ 90 mL/min), mild renal insufficiency (CLcr 60-89 mL/min), and end-stage kidney disease patients on intermittent hemodialysis (IHD) (CLcr < 10 mL/min). The pharmacokinetic parameters assessed included the area under the curve (AUC), maximum concentration (Cmax), clearance rate (CL), volume of distribution (Vz), and half-life (t1/2). Results indicated that subjects with mild renal insufficiency exhibited pharmacokinetic profiles similar to healthy individuals. Nevertheless, in patients undergoing long-term IHD, we observed significant differences: the AUC was 58% higher, Cmax was 29% lower, CL was 42% lower, Vz was 60% larger, and t1/2 was extended by 10 h compared to healthy controls. Secondary outcomes revealed good tolerability of polymyxin B across all groups, with no serious adverse effects related to renal function. In summary, while kidney function may have a slight impact on the pharmacokinetic of polymyxin B, it does not compromise the drug's therapeutic effectiveness.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures

References
-
- Wang Y, Ma Y, Xiong L, et al. Comparison of in vitro synergy between polymyxin B or colistin in combination with 16 antimicrobial agents against multidrug‐resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2024;57:300‐308. - PubMed
-
- Nation RL, Li J, Cars O, et al. Framework for optimisation of the clinical use of colistin and polymyxin B: the Prato polymyxin consensus. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:225‐234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

