Multidisciplinary methodologies used in the study of cable bacteria
- PMID: 39673715
- PMCID: PMC11774119
- DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuae030
Multidisciplinary methodologies used in the study of cable bacteria
Abstract
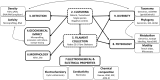
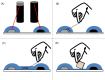
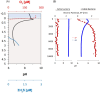
Cable bacteria are a unique type of filamentous microorganism that can grow up to centimetres long and are capable of long-distance electron transport over their entire lengths. Due to their unique metabolism and conductive capacities, the study of cable bacteria has required technical innovations, both in adapting existing techniques and developing entirely new ones. This review discusses the existing methods used to study eight distinct aspects of cable bacteria research, including the challenges of culturing them in laboratory conditions, performing physical and biochemical extractions, and analysing the conductive mechanism. As cable bacteria research requires an interdisciplinary approach, methods from a range of fields are discussed, such as biogeochemistry, genomics, materials science, and electrochemistry. A critical analysis of the current state of each approach is presented, highlighting the advantages and drawbacks of both commonly used and emerging methods.
Keywords: Cable bacteria; enrichment cultures; genomics; microbial community; microprofiling; microscopy.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
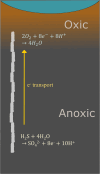


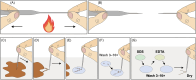
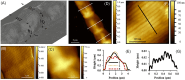
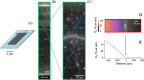
References
-
- Bauman JG, Wiegant J, Borst P et al. A new method for fluorescence microscopical localization of specific DNA sequences by in situ hybridization of fluorochromelabelled RNA. Exp Cell Res. 1980;128:485–90. - PubMed
-
- Berg P, Risgaard-Petersen N, Rysgaard S. Interpretation of measured concentration profiles in sediment pore water. Limnol Oceanogr. 1998;43:1500–10.
-
- Bernkop-Schnürch A, Scerbe-Saiko A. Molecular cloning, expression and purification of recombinant VHH proteins expressed in E. coli. Pharm Res. 1998a;15:263–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

