Lonidamine, a Novel Modulator for the BvgAS System of Bordetella Species
- PMID: 39674913
- PMCID: PMC11873758
- DOI: 10.1111/1348-0421.13193
Lonidamine, a Novel Modulator for the BvgAS System of Bordetella Species
Abstract
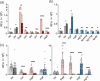
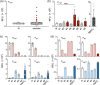
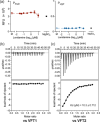
The Gram-negative bacteria Bordetella pertussis, B. parapertussis, and B. bronchiseptica cause respiratory diseases in various mammals. They share the BvgAS two-component system, which regulates the phenotypic conversion between the virulent Bvg+ and avirulent Bvg- phases. In the BvgAS system, the sensor kinase BvgS senses environmental cues and transduces a phosphorelay signal to the response regulator BvgA, which leads to the expression of Bvg+ phase-specific genes, including virulence factor genes. Bacteria grown at 37°C exhibit the Bvg+ phenotype. In contrast, at lower than 26°C or in the presence of modulators, such as MgSO4 and nicotinic acid, the BvgAS system is inactivated, leading bacteria to the avirulent Bvg- phase. Therefore, effective modulators are expected to provide a therapeutic measure for Bordetella infection; however, no such modulators are currently available, and the mechanism by which modulators inactivate the BvgAS system is poorly understood. In the present study, we identified lonidamine as a novel modulator after screening an FDA-approved drug library using bacterial reporter systems with the Bvg+-specific and Bvg--specific promoters. Lonidamine directly bound to the VFT2 domain of BvgS and inactivated the BvgAS system at concentrations as low as 50 nM, which was at least 2000- to 20,000-fold lower than the effective concentrations of known modulators. Lonidamine significantly reduced the adherence of B. pertussis to cultured cells but unexpectedly exacerbated bacterial colonization of the mouse nasal septum. These results provide insights into the structural requirements for BvgAS modulators and the role of Bvg phenotypes in the establishment of infection.
Keywords: Bordetella; BvgAS; lonidamine; modulator; phase conversion.
© 2024 The Author(s). Microbiology and Immunology published by The Societies and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

