Effects of deoxynivalenol contaminated corn distiller's dried grains with solubles on growth performance, body composition, immunological response, and gastrointestinal health in young pullets
- PMID: 39675103
- PMCID: PMC11714707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104611
Effects of deoxynivalenol contaminated corn distiller's dried grains with solubles on growth performance, body composition, immunological response, and gastrointestinal health in young pullets
Abstract
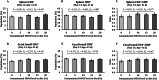
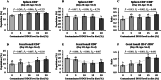
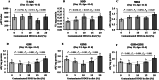
Mycotoxins, particularly deoxynivalenol (DON), are common contaminants in feed ingredients such as corn distiller's dried grains with solubles (DDGS) and pose significant risks to poultry health. This study investigated the effects of feeding naturally DON contaminated DDGS on growth performance, body composition, immunological response, and gastrointestinal health in young pullets. A total of 360, 4-week-old Hy-Line W36 pullets were randomly assigned to diets with increasing levels of naturally DON contaminated DDGS (0, 5, 10, 15, and 20%) over 28 days, resulting in dietary DON concentrations ranging from below the limit of quantification to 15.4 ppm. Diets with DON concentration exceeding 8.9 ppm, corresponding to 15% and 20% DDGS inclusion, resulted in significantly lower body weight gain (BWG) and feed intake (FI) from experimental day 14 to day 28 compared to DON concentration below 5.9 ppm (0, 5 and 10% DDGS groups; P = 0.024 and P = 0.007, respectively). Body composition analysis showed a higher tissue fat percentage in the 20% DDGS group (15.4 ppm DON) by day 28 compared to lower inclusion levels (P = 0.021). Immunologically, a significant increase in the CD4+:CD8+ ratio in spleen was observed in the 20% DDGS group compared to the 0% DDGS group (P = 0.013), whereas both 15 and 20% DDGS inclusion levels significantly increased the ratio in cecal tonsil (P < 0.001). Additionally, interleukin 1β (IL-1β) expression significantly increased in the cecal tonsil by day 28 with 15 and 20% DDGS inclusions (P = 0.002). Gut health was compromised as gut permeability increased linearly with increasing DDGS inclusion (linear, P = 0.043), aligning with significant alterations in the expression of the tight junction protein occludin (OCLN; P = 0.007). Antioxidant responses in the liver showed increased superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in early exposure (day 13, P = 0.038), followed by decreased SOD activity (P = 0.001) and reduced glutathione (GSH) levels (P < 0.001) by day 28. In conclusion, feeding DON-contaminated DDGS at higher inclusion levels (15% and 20%) with final diet DON concentrations exceeding 8.9 ppm over 28 days adversely affects growth performance, immune function, and gut integrity in young pullets.
Keywords: Deoxynivalenol; Gastrointestinal health; Growth performance; Immune response; Pullets.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest There is no conflict of interest.
Figures


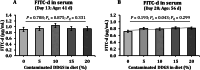

References
-
- Adhikari P.A., Cosby D.E., Cox N.A., Lee J.H., Kim W.K. Effect of dietary bacteriophage supplementation on internal organs, fecal excretion, and ileal immune response in laying hens challenged by Salmonella Enteritidis. Poult. Sci. 2017;96:3264–3271. - PubMed
-
- Andretta I., Kipper M., Lehnen C.R., Hauschild L., Vale M.M., Lovatto P.A. Meta-analytical study of productive and nutritional interactions of mycotoxins in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2011;90:1934–1940. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

