Dysregulation of PI4P in the trans Golgi regions activates the mammalian Golgi stress response
- PMID: 39675715
- PMCID: PMC11770552
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.108075
Dysregulation of PI4P in the trans Golgi regions activates the mammalian Golgi stress response
Abstract
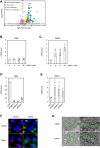
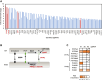
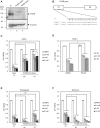
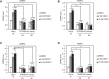
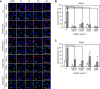
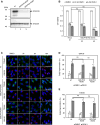
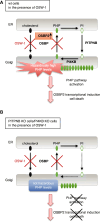
The Golgi stress response is an important cytoprotective system that enhances Golgi function in response to cellular demand, while cells damaged by prolonged Golgi stress undergo cell death. OSW-1, a natural compound with anticancer activity, potently inhibits OSBP that transports cholesterol and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P) at contact sites between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. Previously, we reported that OSW-1 induces the Golgi stress response, resulting in Golgi stress-induced transcription and cell death. However, the underlying molecular mechanism has been unknown. To reveal the mechanism of a novel pathway of the Golgi stress response regulating transcriptional induction and cell death (the PI4P pathway), we performed a genome-wide KO screen and found that transcriptional induction as well as cell death induced by OSW-1 was repressed by the loss of regulators of PI4P synthesis, such as PITPNB and PI4KB. Our data indicate that OSW-1 induces Golgi stress-dependent transcriptional induction and cell death through dysregulation of the PI4P metabolism in the Golgi.
Keywords: Golgi stress response; OSW-1; cancer; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate; the genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 KO screening.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Kimata Y., Kohno K. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-sensing mechanisms in yeast and mammalian cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011;23:135–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

