Global, regional and national disease burden of food-borne trematodiases: projections to 2030 based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
- PMID: 39676162
- PMCID: PMC11648293
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-024-01265-6
Global, regional and national disease burden of food-borne trematodiases: projections to 2030 based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Abstract
Background: Food-borne trematodiases (FBTs), mainly encompassing clonorchiasis, fascioliasis, fasciolopsiasis, opisthorchiasis, and paragonimiasis, is a neglected public health problem, particularly in the WHO South-East Asia and the Western Pacific regions. This study evaluates the global, regional, and national disease burden of FBTs from 1990 to 2021 and projects trends to 2030, underscore the need for targeted prevention and control.
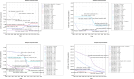
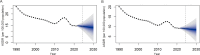
Methods: Using the Global Burden of Disease 2021 database, the crude and the age-standardized prevalence rate (ASPR) and age-standardized prevalence disability-adjusted life years rate (ASDR) of FBTs at the global, regional and national level from 1990 to 2021 were described. The pivotal years of trend changes were identified using joinpoint regression analysis. The effects of age, period, cohort on FBTs prevalence and correlation with the sociodemographic index (SDI) was analyzed. Finally, the worldwide disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for FBTs, projected up to 2030 using the Bayesian age-period-cohort model, were analyzed.
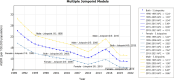
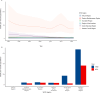
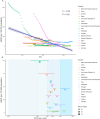
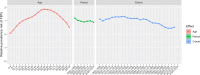
Results: In 2021, 44,466,329 FBTs cases [95% uncertainty interval (UI): 40,017,217, 50,034,921], and 998,028 DALYs [95% UI: 569,766, 1,638,112] were estimated across 17 countries. The Western Pacific region exhibited the highest ASPR and ASDR, with the values of 1649.26 (95% UI: 1461.95, 1881.64) and 36.54 (95% UI: 19.77, 64.16), respectively. From 1990 to 2021, Lao PDR, Thailand, and the Philippines showed the most substantial declines in FBTs, while Kazakhstan had the largest average annual percentage change in DALYs (- 6.60, 95% UI: - 7.10, - 6.10). High-middle and middle SDI countries exhibited higher burden, with ASDR values of 28.03 (95% UI: 15.41, 48.73) and 16.63 (95% UI: 9.32, 27.68), respectively. The disease burden was greater among males, peaking in the 50-59 age group. The projected ASDR in 2030 is 13.10 for males and 8.40 for females.
Conclusions: FBTs remain a public health threat, with the global ASDR projected to remain stable, showing only a slight decrease by 2030. Low-income countries face ambiguous mortality rates and underestimated disease burdens, highlighting the need for improved surveillance. To achieve the 2030 NTD goal, comprehensive surveillance and integrated strategies derived using a One Health approach should be prioritized to control FBTs effectively.
Keywords: Bayesian age-period-cohort analysis model; Disease burden; Food-borne trematodiases.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: Xiao-Nong Zhou is an Editor-in-Chief of the journal Infectious Diseases of Poverty. Guo-jing Yang is an editor of the journal Infectious Diseases of Poverty. They were not involved in the peer-review or handling of the manuscript. The authors have no other competing interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Ending the neglect to attain the sustainable development goals: a road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021–2030. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2020. https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/338565. Accessed 9 July, 2024.
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer: a review of human carcinogens part b: biological agents. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. 2011, Lyon: IARC.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

