Weight and Metabolic Changes With Long-Acting Cabotegravir and Rilpivirine or Bictegravir/Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Alafenamide
- PMID: 39676239
- PMCID: PMC11841724
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003584
Weight and Metabolic Changes With Long-Acting Cabotegravir and Rilpivirine or Bictegravir/Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Alafenamide
Abstract
Background: Modest weight and lipid changes have been observed in cabotegravir plus rilpivirine long-acting (CAB + RPV LA) phase 3/3b studies. The SOLAR study included standardized evaluations of weight and metabolic changes in people living with HIV switching to CAB + RPV LA dosed every 2 months (Q2M) vs. continuing bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (BIC/FTC/TAF).
Setting: Phase 3b, randomized, open-label study conducted in 118 centers across 14 countries.
Methods: Participants (n = 687) were randomized 2:1; 454 switched to CAB + RPV LA Q2M and 227 continued BIC/FTC/TAF. Participants who started lipid-modifying agents or underwent cosmetic procedures were excluded. We analyzed changes in body weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), hip circumference (HC), waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), muscle mass, body fat, and proportion with insulin resistance or metabolic syndrome at 1 year.
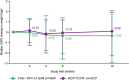
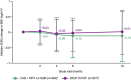
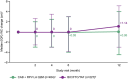
Results: Median (interquartile range) change in body weight from baseline was -0.40 kg (-2.95 to +2.10) and +0.05 kg (-2.30 to +1.95) in the LA and BIC/FTC/TAF arm, respectively. Median (interquartile range) changes in WC and HC were +0.06 cm (-4.50 to 4.00) and +0.00 cm (-4.00 to 3.97) in the LA arm, and +1.14 cm (-3.00 to 5.09) and +0.13 cm (-3.10 to 4.00) in the BIC/FTC/TAF arm. There were no clinically relevant changes in WHtR, WHR, or the proportion with metabolic syndrome or insulin resistance in either arm.
Conclusions: Standardized changes in weight, BMI, and body composition were minor and similar between participant switching to CAB + RPV LA Q2M or continuing BIC/FTC/TAF, with no clinically relevant changes in metabolic syndrome or insulin resistance.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04542070.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Murphy EL, Collier AC, Kalish LA, et al. Highly active antiretroviral therapy decreases mortality and morbidity in patients with advanced HIV disease. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:17–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

