Serum transgelin is a novel prognostic biomarker for COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 39676863
- PMCID: PMC11638039
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1423182
Serum transgelin is a novel prognostic biomarker for COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Background: Transgelin is a central actin-binding protein of the calponin family and involved in the process of multiple pulmonary diseases. Nevertheless, the role of transgelin in Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients is confusing.
Methods: All 317 COVID-19 patients were recruited from two hospital. Peripheral blood was collected from the fasting patients at the onset and convalescent phases. Demographic data and clinical information were obtained. The expression of serum transgelin was estimated using ELISA.
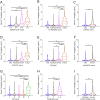
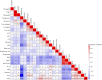
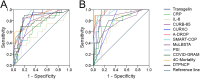
Results: The expression of serum transgelin on admission was gradually elevated in parallel with the increased severity scores of COVID-19. After treatment, serum transgelin expression was reduced during the convalescent phase. Spearman correlative analyses found that serum transgelin expression was closely correlated to lots of clinical parameters. Besides, serum transgelin was positively associated with severity scores. Follow-up research found that serum higher transgelin on admission elevated the risks of mechanical ventilation, vasoactive agent utilization, ICU admission, death, and longer hospital stays during hospitalization through a prospective cohort study. Additionally, there were similarly predictive capacities for critical patients and death between serum transgelin on admission and severity scores among COVID-19 patients.
Conclusions: The expression of serum transgelin is positively with the severity and poorly prognostic outcomes among COVID-19 patients, indicating that transgelin is implicated in the pathological process of COVID-19. Transgelin can assist in the risk stratification and revealing the pathological mechanisms of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; cohort study; prognosis; severity; transgelin.
Copyright © 2024 Gao, Liu, He, Wang, Jiang, Yang, Fu and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

