Breaking barriers: advancing cellular therapies in autoimmune disease management
- PMID: 39676874
- PMCID: PMC11638217
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1503099
Breaking barriers: advancing cellular therapies in autoimmune disease management
Abstract
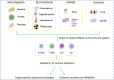
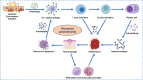
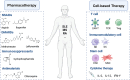
Autoimmune diseases occur due to a dysregulation within the immune system, leading to an aberrant assault on the organism's own tissues. The pathogenesis of these conditions is multifactorial, encompassing intricate interplays among genetic predispositions, environmental determinants, and hormonal fluctuations. The spectrum of autoimmune diseases is broad, impacting a multitude of organ systems, with notable examples such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis (MS), psoriasis, and vitiligo. Despite substantial progress in therapeutic interventions over recent years, a definitive cure for autoimmune diseases has yet to be realized, with existing modalities largely providing palliative care. Cellular therapy is considered the fourth pillar in the management of oncological disorders subsequent to surgical resection, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. Cellular therapies have shown potential in augmenting immune competence and eliminating of targeted neoplastic cells in a spectrum of cancers. As targeting specific molecules on the surface of autoreactive B and T cells, such as CD19, BCMA, CD20, and CTLA-4, cellular therapies are emerging as promising approaches for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. This review delineates the advancements in the application of cellular therapies applied recently for autoimmune diseases and proposes considerations for the advancement of novel therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: B cells; CD19; Tregs; autoimmune diseases; cellular therapy.
Copyright © 2024 Fu, Feng, Qin, Xing, Liu, Liu and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
Author CF was employed by the company Jiangxi Health-Biotech Stem Cell Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Conrad N, Misra S, Verbakel JY, Verbeke G, Molenberghs G, Taylor PN, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and co-occurrence of autoimmune disorders over time and by age, sex, and socioeconomic status: a population-based cohort study of 22 million individuals in the UK. Lancet (London England). (2023) 401:1878–90. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(23)00457-9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials