Analyzing the Effect of Resveratrol on Pharmacokinetics of Antituberculosis Drug Bedaquiline in Rats by a Novel UPLC-MS/MS Approach
- PMID: 39676987
- PMCID: PMC11635514
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07752
Analyzing the Effect of Resveratrol on Pharmacokinetics of Antituberculosis Drug Bedaquiline in Rats by a Novel UPLC-MS/MS Approach
Abstract
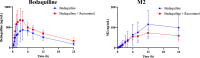
Bedaquiline (BDQ), a diarylquinoline compound, is an inhibitor of mycobacterial ATP synthase, specifically with FDA approval as a treatment for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB). M2 is the main metabolite of BDQ and is active against tuberculosis. The objective of this study was to establish and validate a sensitive and convenient ultraperformance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) approach to concurrently quantify BDQ and M2 in rat plasma and to examine whether resveratrol, a CYP3A4 inhibitor, could influence the pharmacokinetics of BDQ and M2 in rats. Plasma samples containing the internal standard (IS) linezolid were formulated by adding acetonitrile for a simple one-step protein precipitation, and the analytes in samples were quantified by the UPLC-MS/MS method. BDQ and M2 were successfully calibrated in the ranges of 0.5-1000 and 1.0-200 ng/mL, where the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was 0.5 and 1.0 ng/mL, respectively. The precisions and accuracies of BDQ and M2 were in compliance with the FDA analytical standards. Recoveries and matrix effects of the analytes were satisfactory, and the analytes remained stable under four different temperatures and conditions. The well-validated UPLC-MS/MS method was successfully applied to the study of the food-drug interaction in rats. Remarkably, resveratrol increased the level of exposure of BDQ. Furthermore, the effect of resveratrol on the metabolism of BDQ and M2 needs further clinical studies.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coadministration of bedaquiline and pyrifazimine reduce exposure to toxic metabolite N-desmethyl bedaquiline.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 4;14:1154780. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1154780. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37860115 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term plasma pharmacokinetics of bedaquiline for multidrug- and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2019 Jan 1;23(1):99-104. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.18.0042. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2019. PMID: 30674381
-
An LC-MS/MS Bioanalytical Assay for the Determination of Gilteritinib in Rat Plasma and Application to a Drug-Drug Interaction Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 May 26;14:2061-2067. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S243760. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32546970 Free PMC article.
-
A Narrative Review of Bedaquiline and Delamanid: New Arsenals Against Multidrug-Resistant and Extensively Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2024 Aug;38(15-16):e25091. doi: 10.1002/jcla.25091. J Clin Lab Anal. 2024. PMID: 39431709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of resistance and treatment efficacy of clofazimine and bedaquiline against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 10;10:1304857. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1304857. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38274444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resveratrol: Molecular Mechanisms, Health Benefits, and Potential Adverse Effects.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jun 11;6(6):e70252. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70252. eCollection 2025 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40502812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mukherjee J. S.; Rich M. L.; Socci A. R.; Joseph J. K.; Virú F.; Shin S. S.; Furin J. J.; Becerra M. C.; Barry D. J.; Kim J. Y. J. L. Programmes and principles in treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Lancet 2004, 363 (9407), 474–481. - PubMed
-
- Diacon A. H.; Donald P. R.; Pym A.; Grobusch M.; Patientia R. F.; Mahanyele R.; Bantubani N.; Narasimooloo R.; Marez T. D.; van Heeswijk R.; et al. Randomized Pilot Trial of Eight Weeks of Bedaquiline (TMC207) Treatment for Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis: Long-Term Outcome, Tolerability, and Effect on Emergence of Drug Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56 (6), 3271–3276. 10.1128/AAC.06126-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
