A Soft Tissue-Borne Patient-Specific Guide for Foreign Body Removal in the Facial Region
- PMID: 39677233
- PMCID: PMC11646093
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.73698
A Soft Tissue-Borne Patient-Specific Guide for Foreign Body Removal in the Facial Region
Abstract
Foreign body removal in the facial region poses significant challenges due to the complex anatomy and the proximity to critical structures. This study introduces a soft tissue-borne patient-specific guide (PSG) designed to enhance precision and minimize invasiveness in foreign body removal. Four patients underwent foreign body removal using PSGs, with CT and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging employed for segmentation and detailed analysis of both hard and soft tissues. This approach enabled the planning and design of stable and personalized guides. Ultrasound tracing was used for intraoperative verification. All procedures were successful, with minimal scarring, no complications, and reduced operative time. The use of PSGs improved surgical accuracy and efficiency, highlighting their potential for foreign body removal in other regions of the body and for broader clinical applications in maxillofacial surgeries.
Keywords: foreign bodies; minimally invasive surgery; patient-specific guide; soft tissue-borne guide; virtual surgical planning.
Copyright © 2024, Shhadeh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Ethics Committee of the Galilee Medical Center issued approval NHR-0183-23. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
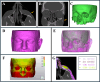
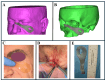
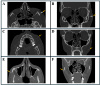
References
-
- Soft tissue foreign body removal with magnet in ED settings. Sarıhan A, Can C. Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32:952–955. - PubMed
-
- Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging: non-invasive imaging. Dill T. Heart. 2008;94:943–948. - PubMed
-
- Management of facial penetrating injury - a case report. Tabariai E, Sandhu S, Alexander G, et al. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68:182–187. - PubMed
-
- Removal of nasal foreign bodies in the pediatric population. Kadish HA, Corneli HM. Am J Emerg Med. 1997;15:54–56. - PubMed
-
- Visibility of foreign bodies in soft tissue in plain radiographs, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and ultrasound. Oikarinen KS, Nieminen TM, Mäkäräinen H, Pyhtinen J. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993;22:119–124. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
