Indian Shot (Canna Indica L). Leaves Provide Valuable Insights into the Management of Inflammation and Other Associated Disorders Offering Health Benefits
- PMID: 39677290
- PMCID: PMC11646432
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S491700
Indian Shot (Canna Indica L). Leaves Provide Valuable Insights into the Management of Inflammation and Other Associated Disorders Offering Health Benefits
Abstract
Background: Throughout history, plants have played a crucial role in advancing medicinal treatments by providing a diverse range of compounds for the development of innovative therapies. Canna indica L. a tropical herb of the Cannaceae family, also known as Indian shot, has a rich history of traditional use in treating ailments like inflammation, malaria, dysentery, fever, dropsy, and diarrhea.
Objective: This comprehensive research invesigates the extract preparation of C. indica leaves using multidisciplinary analytical approaches for this extract in order to shed light on its therapeutic potentials.
Methods: The research, an international collaboration involving researchers from Bangladesh and China, utilized GC-MS/MS analysis to identify bioactive compounds across different C. indica extracts. Biological assays were conducted to assess antimicrobial activity using the disc diffusion method (in vitro), cytotoxicity through the brine shrimp lethality assay (in vitro), analgesic effects via the acetic acid-induced writhing test (in vivo), and antidiarrheal activity with the castor oil-induced diarrhea model (in vivo). Molecular docking studies were performed to determine binding affinities with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR), Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR), Delta Opioid Receptor (DOR), Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α), and Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) receptors.
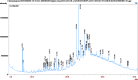
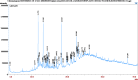
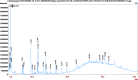
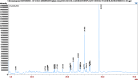
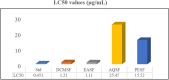
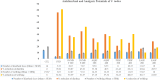
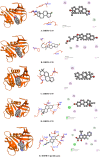
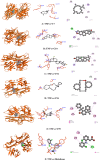
Results: The GC-MS/MS analysis identified 35, 43, 27, and 20 compounds in dichloromethane, aqueous, petroleum ether, and ethyl acetate extracts, respectively. The aqueous (AQSF) and dichloromethane (DCMSF) extracts showed notable antimicrobial activity, particularly against gram-negative bacteria. Cytotoxicity tests indicated that ethyl acetate (EASF) and dichloromethane (DCMSF) fractions were potent. Analgesic activity was highest in DCMSF, and antidiarrheal effects were dose-dependent, with DCMSF showing the greatest efficacy. Molecular docking revealed strong affinities of Ergostane-3,5,6,12,25-pentol, 25-acetate, (3.beta.,5.alpha.,6.beta.,12.beta).- for EGFR and Norgestrel for COX-2.
Conclusion: This research provides valuable insights into the bioactivity evaluation of C. indica, bridging the gap between its chemical composition and diverse biological effects. The findings contribute to the growing body of knowledge in natural product-based drug discovery and underscore the significance of C. indica as a potential source of novel therapeutic agents to treat inflammation and other disease states.
Keywords: Canna indica; GC-MS/MS; analgesic; antidiarrheal; antimicrobial; cytotoxicity; molecular docking.
© 2024 Taher et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Hasan MM, Taher MA, Rahman MA, Muslim T. Analgesic, anti-diarrheal, cns-depressant, membrane stabilizing and cytotoxic activities of canavalia virosa (Roxb.) W&A. Bangladesh Pharm J. 2019;22(2):214–218. doi: 10.3329/bpj.v22i2.42307 - DOI
-
- Pinkey AAH, Khan ZI, Taher MA, Soma MA. Elaeocarpus serratus l. Exhibits potential analgesic and antidiarrheal activities in mice model. Int J. 2020;6(2):44–51.
-
- Hasan MM, Hossain MS, Taher MA, Rahman T. Evaluation of analgesic, antidiarrheal and hypoglycemic activities of wendlandia paniculata (Roxb.) DC leaves extract using mice model. Toxicol Int. 2021;28(2):155–163. doi: 10.18311/ti/2021/v28i2/26775 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

