This is a preprint.
Cortical dynamics in hand/forelimb S1 and M1 evoked by brief photostimulation of the mouse's hand
- PMID: 39677687
- PMCID: PMC11642753
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.02.626335
Cortical dynamics in hand/forelimb S1 and M1 evoked by brief photostimulation of the mouse's hand
Update in
-
Cortical dynamics in hand/forelimb S1 and M1 evoked by brief photostimulation of the mouse's hand.Elife. 2025 May 19;14:RP105112. doi: 10.7554/eLife.105112. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40387088 Free PMC article.
Abstract
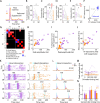
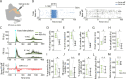
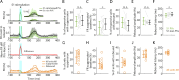
Spiking activity along synaptic circuits linking primary somatosensory (S1) and motor (M1) areas is fundamental for sensorimotor integration in cortex. Circuits along the ascending somatosensory pathway through mouse hand/forelimb S1 and M1 were recently described in detail (Yamawaki et al., 2021). Here, we characterize the peripherally evoked spiking dynamics in these two cortical areas. Brief (5 ms) optogenetic photostimulation of the hand generated short (~25 ms) barrages of activity first in S1 (onset latency 15 ms) then M1 (10 ms later). The estimated propagation speed was 20-fold faster from hand to S1 than from S1 to M1. Amplitudes in M1 were strongly attenuated. Responses were typically triphasic, with suppression and rebound following the initial peak. Evoked activity in S1 was biased to middle layers, consistent with thalamocortical connectivity, while that in M1 was biased to upper layers, consistent with corticocortical connectivity. Parvalbumin (PV) inhibitory interneurons were involved in each phase, accounting for three quarters of the initial spikes generated in S1, and their selective photostimulation sufficed to evoke suppression and rebound in both S1 and M1. Partial silencing of S1 by PV activation during hand stimulation reduced the M1 sensory responses. Overall, these results characterize how evoked spiking activity propagates along the hand/forelimb transcortical loop, and illuminate how in vivo cortical dynamics relate to the underlying synaptic circuit organization in this system.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests - The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures






References
-
- Ahissar E, Sosnik R, Haidarliu S (2000) Transformation from temporal to rate coding in a somatosensory thalamocortical pathway. Nature 406:302–306. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (Methodological) 57:289–300.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
