This is a preprint.
GraphVelo allows for accurate inference of multimodal velocities and molecular mechanisms for single cells
- PMID: 39677753
- PMCID: PMC11642879
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.03.626638
GraphVelo allows for accurate inference of multimodal velocities and molecular mechanisms for single cells
Update in
-
GraphVelo allows for accurate inference of multimodal velocities and molecular mechanisms for single cells.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 22;16(1):7831. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62784-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40847023 Free PMC article.
Abstract
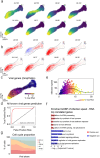
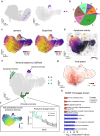
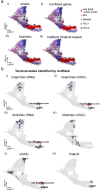
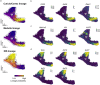
RNA velocities and generalizations emerge as powerful approaches for extracting time-resolved information from high-throughput snapshot single-cell data. Yet, several inherent limitations restrict applying the approaches to genes not suitable for RNA velocity inference due to complex transcriptional dynamics, low expression, or lacking splicing dynamics, or data of non-transcriptomic modality. Here, we present GraphVelo, a graph-based machine learning procedure that uses as input the RNA velocities inferred from existing methods and infers velocity vectors lying in the tangent space of the low-dimensional manifold formed by the single cell data. GraphVelo preserves vector magnitude and direction information during transformations across different data representations. Tests on synthetic and experimental single-cell data including viral-host interactome, multi-omics, and spatial genomics datasets demonstrate that GraphVelo, together with downstream generalized dynamo analyses, extends RNA velocities to multi-modal data and reveals quantitative nonlinear regulation relations between genes, virus and host cells, and different layers of gene regulation.
Figures







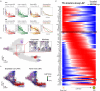

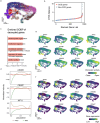

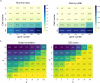

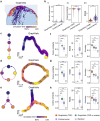


References
-
- Bergen V., Lange M., Peidli S., Wolf F.A. & Theis F.J. Generalizing RNA velocity to transient cell states through dynamical modeling. Nat Biotechnol 38, 1408–1414 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
