This is a preprint.
Macropinocytosis controls metabolic stress-driven CAF subtype identity in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 39677772
- PMCID: PMC11642790
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.11.29.625709
Macropinocytosis controls metabolic stress-driven CAF subtype identity in pancreatic cancer
Update in
-
Macropinocytosis maintains CAF subtype identity under metabolic stress in pancreatic cancer.Cancer Cell. 2025 Sep 8;43(9):1677-1696.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2025.06.021. Epub 2025 Jul 24. Cancer Cell. 2025. PMID: 40712568
Abstract
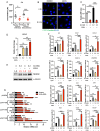
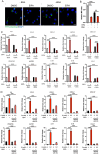
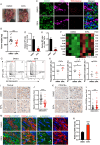
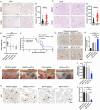
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tumors are deficient in glutamine, an amino acid that tumor cells and CAFs use to sustain their fitness. In PDAC, both cell types stimulate macropinocytosis as an adaptive response to glutamine depletion. CAFs play a critical role in sculpting the tumor microenvironment, yet how adaptations to metabolic stress impact the stromal architecture remains elusive. In this study, we find that macropinocytosis functions to control CAF subtype identity when glutamine is limiting. Our data demonstrate that metabolic stress leads to an intrinsic inflammatory CAF (iCAF) program driven by MEK/ERK signaling. Utilizing in vivo models, we find that blocking macropinocytosis alters CAF subtypes and reorganizes the tumor stroma. Importantly, these changes in stromal architecture can be exploited to sensitize PDAC to immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Our findings demonstrate that metabolic stress plays a role in shaping the tumor microenvironment, and that this attribute can be harnessed for therapeutic impact.
Keywords: CAF heterogeneity; Metabolic stress; drug delivery; macropinocytosis; pancreatic cancer; stromal architecture; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: C.C. is an inventor on a U.S. patent titled “Cancer diagnostics, therapeutics, and drug discovery associated with macropinocytosis,” Patent number: US-11209420-B2. Declaration of interests C.C. is an inventor on a U.S. patent titled “Cancer diagnostics, therapeutics, and drug discovery associated with macropinocytosis,” Patent number: US-11209420-B2.
Figures

References
-
- Sahai E., Astsaturov I., Cukierman E., DeNardo D.G., Egeblad M., Evans R.M., Fearon D., Greten F.R., Hingorani S.R., Hunter T., et al. (2020). A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nature reviews. Cancer 20, 174–186. 10.1038/s41568-019-0238-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
