This is a preprint.
Cutaneous human papillomavirus E6 impairs the cGAS-STING pathway
- PMID: 39677810
- PMCID: PMC11642751
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.11.29.625575
Cutaneous human papillomavirus E6 impairs the cGAS-STING pathway
Abstract
Beta genus human papillomaviruses (β-HPVs) are ubiquitous double stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses that may promote skin cancers by destabilizing the host genome. Supporting this, expression of the E6 gene from a β-HPV (β-HPV 8 E6) results in increased micronuclei that should induce an innate immune response that eliminates these cells. Yet, β-HPV 8 E6 promotes rather than restricts proliferation. We hypothesize that β-HPV 8 E6 accomplishes this by attenuating the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) pathway, an innate immune pathway that becomes activated in response to cytosolic micronuclear dsDNA. Here, we show that in response to stimulation by transfection of pLVX-GFP plasmid, β-HPV 8 E6 reduced the magnitude and intensity of cGAS-STING pathway activation in immunoblot experiments. These data also demonstrate that impairment of the cGAS-STING pathway is strongest downstream of STING phosphorylation. Further, RNA-sequencing suggests that β-HPV 8 E6 downregulates other innate immune pathways. We also show that cGAS is recruited to micronuclei induced by β-HPV 8 E6. These data suggest a mechanism by which β-HPV 8 E6 facilitates proliferation of cells destabilized by micronuclei and support the hypothesis that the prevalence of β-HPV infections is in part due to the impairment of the cGAS-STING innate immune response.
Figures


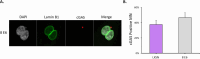

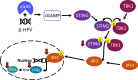
References
-
- Albertini S., Lo Cigno I., Calati F., De Andrea M., Borgogna C., Dell’Oste V., Landolfo S., & Gariglio M. (2018). HPV18 Persistence Impairs Basal and DNA Ligand–Mediated IFN-β and IFN-λ1 Production through Transcriptional Repression of Multiple Downstream Effectors of Pattern Recognition Receptor Signaling. The Journal of Immunology, 200(6), 2076–2089. 10.4049/jimmunol.1701536 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Babraham Bioinformatics—FastQC A Quality Control tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. (n.d.). Retrieved September 4, 2024, from https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/
-
- Chiang C., Pauli E.-K., Biryukov J., Feister K. F., Meng M., White E. A., Münger K., Howley P. M., Meyers C., & Gack M. U. (2018). The Human Papillomavirus E6 Oncoprotein Targets USP15 and TRIM25 To Suppress RIG-I-Mediated Innate Immune Signaling. Journal of Virology, 92(6), 10.1128/jvi.01737–17. 10.1128/jvi.01737-17 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
