SoC estimation on Li-ion batteries: A new EIS-based dataset for data-driven applications
- PMID: 39678444
- PMCID: PMC11639334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2024.110947
SoC estimation on Li-ion batteries: A new EIS-based dataset for data-driven applications
Abstract
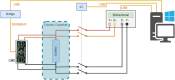
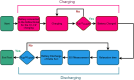
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are crucial in numerous applications, including portable electronics, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) is a powerful technique for characterizing batteries, providing valuable insights into charge transfer kinetics like ion diffusion and interfacial reactions. However, obtaining comprehensive and diverse datasets for battery State of Charge (SoC) studies remains challenging due to the complex nature of battery operations and the time-intensive testing process. This paper presents a novel and original EIS dataset specifically designed for 600 mAh capacity Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries at various SoC levels. The dataset includes repeated EIS measurements using different battery discharging cycles, allowing researchers to examine the frequency domain properties and develop data-driven algorithms for assessing battery SoC and predicting performance. The data acquisition system employs a battery specific impedance meter and an electronic load, ensuring accurate and controlled measurements. The dataset, comprising EIS measurements from multiple LFP batteries, serves as a valuable resource for researchers in the fields of battery technology, electrochemistry, power sources, and energy storage. Moreover, industries such as consumer electronics, power systems, and electric transportation can benefit from the dataset's insights for effectively managing rechargeable battery devices. The presented dataset expands the scope of impedance spectroscopy measurements and holds significant potential for future applications and advancements in Li-ion battery technologies.
Keywords: Dataset; Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; LFP batteries; State of charge.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Figures





References
-
- Zubi G., et al. The lithium-ion battery: State of the art and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018;89:292–308.
-
- Zhao T., et al. An overview on the life cycle of lithium iron phosphate: synthesis, modification, application, and recycling. Chem. Eng. J. 2024
-
- Christensen A.Paul, et al. Risk management over the life cycle of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021;148
-
- Ding Y., et al. Automotive Li-ion batteries: current status and future perspectives. Electrochem. Energ. Rev. 2019;2:1–28.
-
- Islam S.M Rakiul, Park Sung-Yeul, Balasingam Balakumar. 2018 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC) IEEE; 2018. Circuit parameters extraction algorithm for a lithium-ion battery charging system incorporated with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

