Valorisation of sawdust-based spent mushroom substrate for sustainable xylooligosaccharides production using low-cost crude xylanases from Aspergillus flavus KUB2
- PMID: 39678636
- PMCID: PMC11636150
- DOI: 10.1080/21501203.2024.2305719
Valorisation of sawdust-based spent mushroom substrate for sustainable xylooligosaccharides production using low-cost crude xylanases from Aspergillus flavus KUB2
Abstract
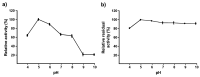
Spent mushroom substrate (SMS), a lignocellulosic waste after mushroom production is generally discarded without proper management. There is increasing interest in the sustainable transformation of lignocellulosic waste into high-value products. Within this context, the present study investigated the potential of the SMS from the cultivation of Pleurotus pulmonarius and Auricularia auricula on rubber tree wood sawdust as substrates for xylooligosaccharides (XOS) production. SMS samples from these two edible mushrooms were extracted using alkaline xylan extraction, producing maximum true recovery amounts of xylan in the range 34.61%-37.49% using 18% NaOH at 70 °C for 3 h. Production of XOS from alkaline-extracted xylan from the SMS samples of both mushroom species using economically crude xylanases from Aspergillus flavus KUB2 resulted in XOS (X2-X5) production of 241.47-249.04 mg/g, with X3 as the predominant XOS product. The produced XOS had excellent prebiotic activity and 2,2'-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity and contained high total phenolic contents. The combined beneficial bioactivities in terms of prebiotic and antioxidant properties suggested that the XOS produced from sawdust-based SMS samples of P. pulmonarius and A. auricula could be promising ingredients for both food and pharmaceutical applications.
Keywords: Aspergillus flavus; Spent mushroom substrate; antioxidant activity; prebiotic; xylan; xylooligosaccharides.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





References
-
- Ávila PF, Martins M, de Almeida Costa FA, Goldbeck R. 2020. Xylooligosaccharides production by commercial enzyme mixture from agricultural wastes and their prebiotic and antioxidant potential. Bioact Carbohydr Diet Fibre. 24:100234. doi: 10.1016/j.bcdf.2020.100234. - DOI
-
- Bae JS, Kim IY, Jung SH, Oh YG, Kwak WS. 2006. Evaluation on feed-nutritional value of spent mushroom (Pleurotus osteratus, Pleurotus eryngii, Flammulina velutipes substrates as a roughage source for ruminants). J Anim Sci Technol. 48:237–246.
-
- Bailey MJ, Biely P, Poutanen K. 1992. Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J Biotechnol. 23(3): 257–270. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(92)90074-J. - DOI
-
- Banerjee S, Patti AF, Ranganathan V, Arora A. 2019. Hemicellulose based biorefinery from pineapple peel waste: Xylan extraction and its conversion into xylooligosaccharides. Food Bioprod Process. 117:38–50. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2019.06.012. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
