Treating deep sternal wound infection with pectoralis major flap transposition: a systemic factor analysis of efficacy and safety
- PMID: 39678841
- PMCID: PMC11635220
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-1490
Treating deep sternal wound infection with pectoralis major flap transposition: a systemic factor analysis of efficacy and safety
Abstract
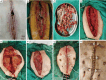
Background: Deep sternal wound infection (DSWI) is a life-threatening postoperative complication of cardiac surgery. Currently, there are many therapies used to treat patients with DSWI. However, none of these therapies have been shown to be the optimal choice for patients with DSWI. Additionally, these methods may require additional facilities which limit their widespread use. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the effectiveness, safety, and risk factors related to the prognosis of DSWI patients treated with pectoralis major flap transposition (PMFT), a more concise method.
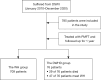
Methods: A retrospective, systemic analysis was conducted of DSWI patients at the Beijing Anzhen Hospital from January 2010 until December 2020. All the patients were diagnosed with DSWI according to the relevant guidelines, and treated with PMFT. The patients were divided into the following two groups based on their prognosis after treatment with PMFT: (I) the wound healing (WH) group; and (II) the delayed wound healing or death (DWHD) group. All the participants were followed up for 1 year.
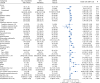
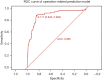
Results: In total, 9.7% (76/785) of the DSWI patients experienced DWHD in the present study. The all-cause mortality rate was 3.7% (29/785). While 90.3% (709/785) of the patients achieved WH after undergoing PMFT. The multivariate logistic regression model indicated that patients with diabetes mellitus, obesity, a history of smoking, abnormal liver function, anemia, chronic infection, immune disease, hypothermia, a longer gap time, and patients requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) assistance, salvage surgery, and secondary cardiac surgery were more likely to experience DWDH.
Conclusions: This study showed PMFT was a safe and effective method for treating DSWI after cardiac surgery. Patients with risk factors, such as those mentioned above, require more attention. Prospective studies should be conducted to explore the relationships among the novel risk factors and DSWI.
Keywords: Deep sternal wound infection (DSWI); cardiac surgery; efficacy; pectoralis major flap; safety.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-1490/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
