Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Advanced Biomedical Engineering Applications
- PMID: 39679058
- PMCID: PMC11638789
- DOI: 10.1021/acspolymersau.4c00028
Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Advanced Biomedical Engineering Applications
Abstract
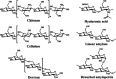
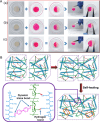
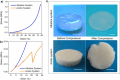
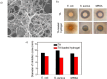
In recent years, numerous applications of hydrogels using polysaccharides have evolved, benefiting from their widespread availability, excellent biodegradability, biocompatibility, and nonpoisonous nature. These natural polymers are typically sourced from renewable materials or from manufacturing processes, contributing collaboratively to waste management and demonstrating the potential for enhanced and enduring sustainability. In the field of novel bioactive molecule carriers for biotherapeutics, natural polymers are attracting attention due to their inherent properties and adaptable chemical structures. These polymers offer versatile matrices with a range of architectures and mechanical properties, while retaining the bioactivity of incorporated biomolecules. However, conventional polysaccharide-based hydrogels suffer from inadequate mechanical toughness with large swelling properties, which prohibit their efficacy in real-world applications. This review offers insights into the latest advancements in the development of diverse polysaccharide-based hydrogels for biotherapeutic administrations, either standalone or in conjunction with other polymers or drug delivery systems, in the pharmaceutical and biomedical fields.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Shakil A. R.; Begum M. L.; Shaikh M. A. A.; Sultana S.; Rumon M. M. H.; Rahman M. S.; Roy C. K.; Haque M. A. Jute Fiber Reinforced Hydrogel Composite for Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Water. Dhaka Univ. J. Sci. 2022, 70 (2), 59–64. 10.3329/dujs.v70i2.62608. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
