Body Surface Potential Mapping: A Perspective on High-Density Cutaneous Electrophysiology
- PMID: 39679757
- PMCID: PMC11775574
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202411087
Body Surface Potential Mapping: A Perspective on High-Density Cutaneous Electrophysiology
Abstract
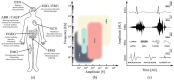
The electrophysiological signals recorded by cutaneous electrodes, known as body surface potentials (BSPs), are widely employed biomarkers in medical diagnosis. Despite their widespread application and success in detecting various conditions, the poor spatial resolution of traditional BSP measurements poses a limit to their diagnostic potential. Advancements in the field of bioelectronics have facilitated the creation of compact, high-quality, high-density recording arrays for cutaneous electrophysiology, allowing detailed spatial information acquisition as BSP maps (BSPMs). Currently, the design of electrode arrays for BSP mapping lacks a standardized framework, leading to customizations for each clinical study, limiting comparability, reproducibility, and transferability. This perspective proposes preliminary design guidelines, drawn from existing literature, rooted solely in the physical properties of electrophysiological signals and mathematical principles of signal processing. These guidelines aim to simplify and generalize the optimization process for electrode array design, fostering more effective and applicable clinical research. Moreover, the increased spatial information obtained from BSPMs introduces interpretation challenges. To mitigate this, two strategies are outlined: observational transformations that reconstruct signal sources for intuitive comprehension, and machine learning-driven diagnostics. BSP mapping offers significant advantages in cutaneous electrophysiology with respect to classic electrophysiological recordings and is expected to expand into broader clinical domains in the future.
Keywords: BSPM; electrophysiology; high‐density; mapping; wearables.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H., Jessell T. M., Siegelbaum S. A., Hudspeth A. J., Principles of Neural Science, McGraw‐Hill, New York, NY, 2013.
-
- Alberts B., Johnson A., Lewis J., Raff M., Roberts K., Walter P., Molecular Biology of the Cell, Garland Science, New York, NY, 2014.
-
- Guyton A. C., Hall J. E., Textbook of Medical Physiology, Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA, 2020.
-
- Sperelakis N., Freedman J. C., Cell Physiology Source Book, Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 2011.
-
- Stein W. D., Membrane Physiology, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
