This is a preprint.
Loss of Pigment Epithelium Derived Factor Sensitizes C57BL/6J Mice to Light-Induced Retinal Damage
- PMID: 39679905
- PMCID: PMC11643041
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.12.04.626802
Loss of Pigment Epithelium Derived Factor Sensitizes C57BL/6J Mice to Light-Induced Retinal Damage
Abstract
Purpose: Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is a neurotrophic glycoprotein secreted by the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) that supports retinal photoreceptor health. Deficits in PEDF are associated with increased inflammation and retinal degeneration in aging and diabetic retinopathy. We hypothesized that light-induced stress in C57BL/6J mice deficient in PEDF would lead to increased retinal neuronal and RPE defects, impaired expression of neurotrophic factor Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and overactivation of Galectin-3-mediated inflammatory signaling.
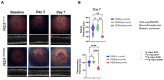
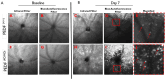
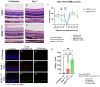
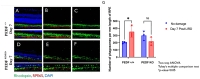
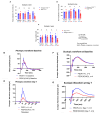
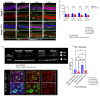
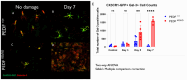
Methods: C57BL/6J mice expressing the RPE65 M450/M450 allele were crossed to PEDF KO/KO and wildtype (PEDF +/+) littermates. Mice were exposed to 50,000 lux light for 5 hours to initiate acute damage. Changes in visual function outcomes were tracked via electroretinogram (ERG), confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy(cSLO), and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) on days 3, 5, and 7 post-light exposure. Gene and protein expression of Galectin-3 were measured by digital drop PCR (ddPCR) and western blot. To further investigate the role of galectin-3 on visual outcomes and PEDF expression after damage, we also used a small-molecule inhibitor to reduce its activity.
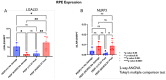
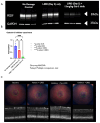
Results: Following light damage, PEDF KO/KO mice showed more severe retinal thinning, impaired visual function (reduced a-, b-, and c-wave amplitudes), and increased Galectin-3 expressing immune cell infiltration compared to PEDF +/+. PEDF KO/KO mice had suppressed damage-associated increases in IGF-1 expression. Additionally, baseline Galectin-3 mRNA and protein expression were reduced in PEDF KO/KO mice compared to PEDF +/+. However, after light damage, Galectin-3 expression decreases in PEDF +/+ mice but increases in PEDF KO/KO mice without reaching PEDF +/+ levels. Galectin-3 inhibition worsens retinal degeneration, reduces PEDF expression in PEDF +/+ mice, and mimics the effects seen in PEDF knockouts.
Conclusions: Loss of PEDF alone does not elicit functional defects in C57BL/6J mice. However, under light stress, PEDF deficiency significantly increases severe retinal degeneration, visual deficits, Galectin-3 expression, and suppression of IGF-1 than PEDF +/+. PEDF deficiency reduced baseline expression of Galectin-3, and pharmacological inhibition of Galectin-3 worsens outcomes and suppresses PEDF expression in PEDF +/+, suggesting a novel co-regulatory relationship between the two proteins in mitigating light-induced retinal damage.
Figures

References
-
- Jablonski MM, Tombran-Tink J, Mrazek DA, Iannaccone A. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Supports Normal Development of Photoreceptor Neurons and Opsin Expression after Retinal Pigment Epithelium Removal. The Journal of Neuroscience 2000;20:7149. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-19-07149.2000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tombran-Tink J, Mazuruk K, Rodriguez IR, Chung D, Linker T, Englander E, et al. Organization, Evolutionary Conservation, Expression and Unusual Alu Density of the Human Gene for Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor, a Unique Neurotrophic Serpin. Molecular Vision. 1996. URL: http://www.molvis.org/molvis/v2/a11/ (Accessed 22 July 2024). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
