Long-Term Treatment Outcomes of Micropulse Transscleral Cyclophotocoagulation in Primary and Secondary Glaucoma: A 5-Year Analysis
- PMID: 39680324
- PMCID: PMC11754562
- DOI: 10.1007/s40123-024-01080-0
Long-Term Treatment Outcomes of Micropulse Transscleral Cyclophotocoagulation in Primary and Secondary Glaucoma: A 5-Year Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: To investigate 5-year outcomes on intraocular pressure (IOP) and safety of micropulse transscleral cyclophotocoagulation (TSCPC) in patients with glaucoma.
Methods: Patients with mild to advanced glaucoma who underwent a standardized micropulse TSCPC procedure at the University Eye Clinic Maastricht from November 2016 to February 2019 were included.
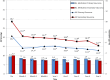
Results: A total of 165 eyes were included, with outcomes for 112 eyes available after 5-year follow-up. Mean age was 67.3 ± 13.9 years; 58.2% were male. Glaucoma subtypes were primary glaucoma (n = 108) and secondary glaucoma (n = 57). Prior glaucoma surgery was performed in 65 of 165 eyes (39.4%). In the primary glaucoma group, mean preoperative IOP was 20.7 ± 7.1 mmHg. Mean postoperative IOP at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years significantly reduced to 15.2 ± 6.5, 14.3 ± 5.0, 14.0 ± 4.9, 13.5 ± 4.1, and 12.9 ± 4.3 mmHg, respectively. Preoperatively, the mean number of IOP-lowering medications was 3.3 ± 1.3, which changed to 2.8 ± 1.3, 2.8 ± 1.2, 2.8 ± 1.2, 2.9 ± 1.2, and 2.7 ± 1.3 at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years, respectively. In the secondary glaucoma group, mean preoperative IOP was 28.7 ± 10.3 mmHg, dropping significantly to 19.3 ± 10.4, 18.6 ± 11.3, 17.8 ± 9.8, 18.1 ± 12.0, and 15.5 ± 7.6 mmHg at the same intervals. The number of IOP-lowering medication was significantly reduced from 3.5 ± 1.1 to 2.5 ± 1.5, 2.2 ± 1.5, 2.6 ± 1.4, 2.6 ± 1.5, and 2.5 ± 1.7. In the total group, mean IOP reduction was 32.5% after 5 years. Postoperative complications included cystic macular edema (n = 3), fibrinous/uveitic reaction (n = 1), and rejection of corneal graft (n = 2), all reversible after treatment. One patient developed late and persisting hypotony. Other adverse events were retinal venous occlusion (n = 1) and retinal vasculitis (n = 1), unrelated to the laser treatment. In patients with a preoperative Central Distance Visual Acuity (CDVA) > 0.05 on the Snellen chart, more than two lines of visual acuity (VA) loss were attributed to cataract (n = 10), retinal disease (n = 5), glaucoma progression (n = 3), corneal decompensation (n = 2), or other factors (n = 11).
Conclusion: Micropulse TSCPC is a safe and effective treatment for reducing IOP and the number of IOP-lowering medications after a 5-year follow-up period. It is a viable alternative for patients after failed incisional glaucoma surgery or high-risk patients.
Keywords: Glaucoma; Laser treatment; Micropulse; Transscleral cyclophotocoagulation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: Ronald M.P.C. de Crom has received speaker honorarium from IRIDEX Corporation. Stefani Kujovic-Aleksov, Carroll A.B. Webers, Tos T.J.M. Berendschot, and Henny J.M. Beckers declare that they have no competing interests. Ethical Approval: This study was conducted according to guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards and was approved by the institutional ethics committee (METC) operating at the Maastricht University Medical Centre + in Maastricht, The Netherlands, No METC 2020-2404 (24-12-2020). All patients gave informed consent prior to undergoing treatment.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

