Physical One-Way Functions for Decentralized Consensus Via Proof of Physical Work
- PMID: 39680720
- PMCID: PMC11791968
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202409386
Physical One-Way Functions for Decentralized Consensus Via Proof of Physical Work
Abstract
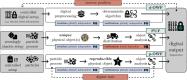
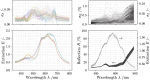
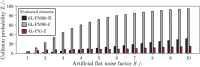
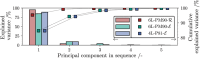
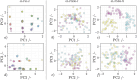
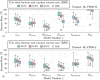
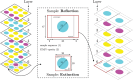
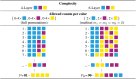
Decentralized consensus on the state of the Bitcoin blockchain is ensured by proof of work. It relies on digital one-way functions and is associated with an enormous environmental impact. This paper conceptualizes a physical one-way function that aims to transform a digital, electricity-consuming consensus mechanism into a physical process. Boundary conditions for the security requirements are established and discussed as well as experimentally investigated for a specific setup based on printing and optical analysis of pigment-carrier composites. In the context of the applied methods, this setup promises to be mathematically unclonable, steady, reproducible, collision resistant and non-invertible and illustrates the feasibility of a physical one-way function. Based on this, a framework for proof of physical work is conceptualized, which has the potential of a drastically lower CO2 footprint. This work initiates a progressive, interdisciplinary field of research and demands further investigations with regards to alternative setups, security definitions and strategies for challenging them.
Keywords: cryptography; decentralized consensus; physical one‐way function; proof of work.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Frank Kleine Jäger, Lothar Seidemann and Holger Jelich are currently employed by the funding organization BASF and involved in certain related patents. All other authors affiliated with KIT declare no financial or non‐financial competing interests and are not associated with any of the patents. The experimental investigations and data analysis were performed at KIT without any governance or control of BASF and associated authors. Hence, the conducted research is unbiased by financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Secure hash standard (SHS) (FIPS 180‐4), Standard, National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2015.
-
- Nakamoto S., Bitcoin: A peer‐to‐peer electronic cash system, https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf (accessed: October 2024).
-
- Küfeoğlu S., Özkuran M., Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2019, 58, 101273.
-
- de Vries A., Gallersdörfer U., Klaaßen L., Stoll C., Joule 2022, 6, 498.
-
- Baker G. L., Gollub J. P., Chaotic Dynamics: An Introduction, 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 1996.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
