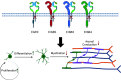
Revisiting the role of ErbBs in oligodendrocyte development
- PMID: 39680783
- PMCID: PMC11670055
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2422181121
Revisiting the role of ErbBs in oligodendrocyte development
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The author declares no competing interest.
Figures
Comment on
-
Pan-ErbB inhibition impairs cognition via disrupting myelination and aerobic glycolysis in oligodendrocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 5;121(45):e2405152121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2405152121. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39475641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nave K. A., Ehrenreich H., Myelination and oligodendrocyte functions in psychiatric diseases. JAMA Psychiatry 71, 582–584 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Stadelmann C., Timmler S., Barrantes-Freer A., Simons M., Myelin in the central nervous system: Structure, function, and pathology. Physiol. Rev. 99, 1381–1431 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Nave K. A., Salzer J. L., Axonal regulation of myelination by neuregulin 1. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 16, 492–500 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources