Current Treatment Methods in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 39682245
- PMCID: PMC11640602
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16234059
Current Treatment Methods in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
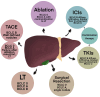
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a prevalent malignant tumour worldwide. Depending on the stage of the tumour and liver function, a variety of treatment options are indicated. Traditional radiotherapy and chemotherapy are ineffective against HCC; however, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved radiofrequency ablation (RFA), surgical resection, and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for advanced HCC. On the other hand, liver transplantation is recommended in the early stages of the disease. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) like lenvatinib and sorafenib, immunotherapy and anti-angiogenesis therapy, including pembrolizumab, bevacizumab, tremelimumab, durvalumab, camrelizumab, and atezolizumab, are other treatment options for advanced HCC. Moreover, to maximize outcomes for patients with HCC, the combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) along with targeted therapies or local ablative therapy is being investigated. This review elaborates on the current status of HCC treatment, outlining the most recent clinical study results and novel approaches.
Keywords: TACE; TARE; atezolizumab; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunotherapy; lenvatinib; nivolumab; pembrolizumab; radiation therapy; sorafenib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Asafo-Agyei K.O., Samant H. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; St. Petersburg, FL, USA: 2024. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous