Role of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases in Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Celiac Disease and Diabetes: Focus on the Intestinal Mucosa
- PMID: 39682729
- PMCID: PMC11640621
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13231981
Role of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases in Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Celiac Disease and Diabetes: Focus on the Intestinal Mucosa
Abstract
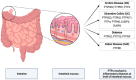
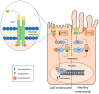
Protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) are a family of enzymes essential for numerous cellular processes, such as cell growth, inflammation, differentiation, immune-mediated responses and oncogenic transformation. The aim of this review is to review the literature concerning the role of several PTPs-PTPN22, PTPN2, PTPN6, PTPN11, PTPσ, DUSP2, DUSP6 and PTPRK-at the level of the intestinal mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), celiac disease (CeD) and type 1 diabetes (T1D) in both in vitro and in vivo models. The results revealed shared features, at the level of the intestinal mucosa, between these diseases characterized by alterations of different biological processes, such as proliferation, autoimmunity, cell death, autophagy and inflammation. PTPs are now actively studied to develop new drugs. Also considering the availability of organoids as models to test new drugs in personalized ways, it is very likely that soon these proteins will be the targets of useful drugs.
Keywords: celiac disease; diabetes; inflammatory bowel diseases; intestinal mucosa; protein tyrosine phosphatases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

