Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activities of Essential Oil from Citrus reticulata Blanco cv. Tankan Peel Against Listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 39682912
- PMCID: PMC11640327
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13233841
Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activities of Essential Oil from Citrus reticulata Blanco cv. Tankan Peel Against Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
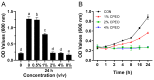
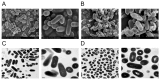
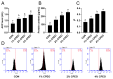
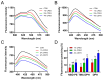
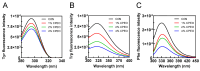
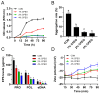
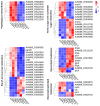
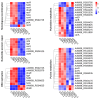
In recent years, plant essential oils have been confirmed as natural inhibitors of foodborne pathogens. Citrus reticulata Blanco cv. Tankan peel essential oil (CPEO) showed anti-Listeria monocytogenes (LM) activities, and this study investigated the associated mechanisms by using high-resolution electron microscope, fluorescence spectrometer, flow cytometer, potentiometer, and transcriptome sequencing. The results showed that CPEO restrained LM growth at a minimum inhibitory concentration of 2% (v/v). The anti-LM abilities of CPEO were achieved by disrupting the permeability of the cell wall, damaging the permeability, fluidity, and integrity of the cell membrane, disturbing the membrane hydrophobic core, and destroying the membrane protein conformation. Moreover, CPEO could significantly inhibit the LM aggregation from forming biofilm by reducing the extracellular polymeric substances' (protein, polysaccharide, and eDNA) production and bacterial surface charge numbers. The RNA sequencing data indicated that LM genes involved in cell wall and membrane biosynthesis, DNA replication and repair, quorum sensing and two-component systems were expressed differently after CPEO treatment. These results suggested that CPEO could be used as a novel anti-LM agent and green preservative in the food sector. Further studies are needed to verify the anti-LM activities of CPEO in real food.
Keywords: Listeria monocytogenes; biofilm; cell membrane; essential oils; extracellular polymeric substances; transcriptome analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Jie Ren was employed by the company Nuspower Greatsun (Guangdong) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. He participated in conceptualization, validation, and investigation in the study. The role of the company was Vice president of R&D. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Citrus lemon essential oil: chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities with its preservative effect against Listeria monocytogenes inoculated in minced beef meat.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Aug 3;16(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0487-5. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28774297 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Oxygenated Heterocyclic Compounds and in vitro Antioxidant Activity of Pomelo Essential Oil.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Mar 2;15:937-947. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S299678. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 33688168 Free PMC article.
-
Tandem mass tag-based quantitative proteomic analysis reveal the inhibition mechanism of thyme essential oil against flagellum of Listeria monocytogenes.Food Res Int. 2019 Nov;125:108508. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108508. Epub 2019 Jun 22. Food Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31554054
-
Insights into the chemical composition and bioactivities of citrus peel essential oils.Food Res Int. 2021 May;143:110231. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110231. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Food Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33992345 Review.
-
Citrus Essential Oils: a Treasure Trove of Antibiofilm Agent.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2022 Oct;194(10):4625-4638. doi: 10.1007/s12010-022-04033-0. Epub 2022 Jul 2. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35779176 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential Oils for Biofilm Control: Mechanisms, Synergies, and Translational Challenges in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 May 13;14(5):503. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14050503. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40426569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a TonB-Dependent Siderophore Receptor as a Novel Anti-Biofilm Target and Virtual Screening for Its Inhibitor in Pseudomonas fluorescens PF08.Foods. 2025 Feb 6;14(3):531. doi: 10.3390/foods14030531. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39942124 Free PMC article.
-
Linalool as a potential agent for inhibiting Escherichia coli biofilm formation and exopolysaccharide production.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Apr 2;21(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04681-4. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40169959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silva N.F.D., Neves M.M.P.S., Magalhães J.M.C.S., Freire C., Delerue-Matos C. Emerging electrochemical biosensing approaches for detection of Listeria monocytogenes in food samples: An overview. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020;99:621–633. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.03.031. - DOI
-
- Zamuz S., Munekata P.E.S., Dzuvor C.K.O., Zhang W., Sant’Ana A.S., Lorenzo J.M. The role of phenolic compounds against Listeria monocytogenes in food. A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021;110:385–392. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.068. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 32402274/Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023KTSCX051/Guangdong Universities Characteristic Innovation Project
- 2021A1515110660/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- SL2022A04J01086/Guangzhou Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- Heyuan2021016/Guangdong Science and Technology Special Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

